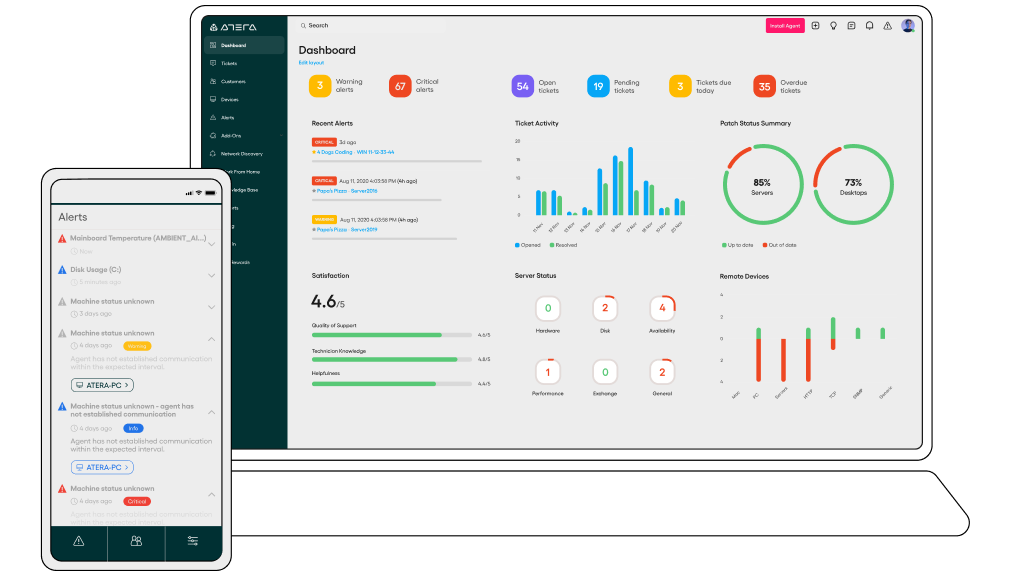
RMM remote management has revolutionized how IT professionals manage and monitor their systems. This powerful technology allows for efficient, proactive, and secure control over remote devices, empowering organizations to optimize performance, enhance security, and reduce downtime.
Table of Contents
By leveraging RMM solutions, IT teams gain real-time visibility into their infrastructure, enabling them to identify and address issues before they escalate. This proactive approach significantly improves IT efficiency, reduces costs associated with reactive troubleshooting, and ensures uninterrupted operations.
RMM Overview
Remote management and monitoring (RMM) solutions have become indispensable tools for businesses of all sizes, streamlining IT operations and ensuring the smooth functioning of critical systems. RMM software empowers IT professionals to remotely manage and monitor devices, networks, and applications, providing valuable insights into system health and performance.
Key Features and Benefits
RMM solutions offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to simplify IT management and enhance operational efficiency.
- Remote Access and Control: RMM enables IT teams to access and control devices remotely, troubleshooting issues and deploying software updates without needing to physically visit the location. This capability significantly reduces downtime and improves response times to critical incidents.
- Automated Patch Management: RMM solutions automate the process of patching operating systems and software applications, ensuring devices are protected from vulnerabilities and security threats. This feature significantly reduces the risk of security breaches and malware infections.
- Performance Monitoring and Reporting: RMM software provides real-time insights into device and network performance, allowing IT professionals to identify bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and proactively address potential issues before they impact operations.
- Alerting and Notifications: RMM solutions generate alerts and notifications when critical events occur, such as system failures, hardware malfunctions, or security threats. This proactive approach allows IT teams to address issues promptly, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
- Security and Compliance: RMM software includes security features such as endpoint security, antivirus protection, and data encryption, safeguarding devices and sensitive information from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
Industries and Organizations
RMM solutions are widely adopted across various industries and organizations, including:
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs): MSPs rely heavily on RMM solutions to manage and monitor the IT infrastructure of their clients, providing comprehensive support and maintenance services.
- Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs): SMBs often lack dedicated IT staff and benefit from RMM solutions to simplify IT management, reduce costs, and ensure business continuity.
- Large Enterprises: Large enterprises with extensive IT infrastructure use RMM solutions to manage and monitor their vast network of devices and applications, ensuring optimal performance and security.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations rely on RMM solutions to manage medical devices, electronic health records (EHRs), and other critical systems, ensuring patient safety and compliance with industry regulations.
- Education: Educational institutions use RMM to manage student devices, network infrastructure, and learning platforms, providing a secure and reliable learning environment.
RMM Functionality
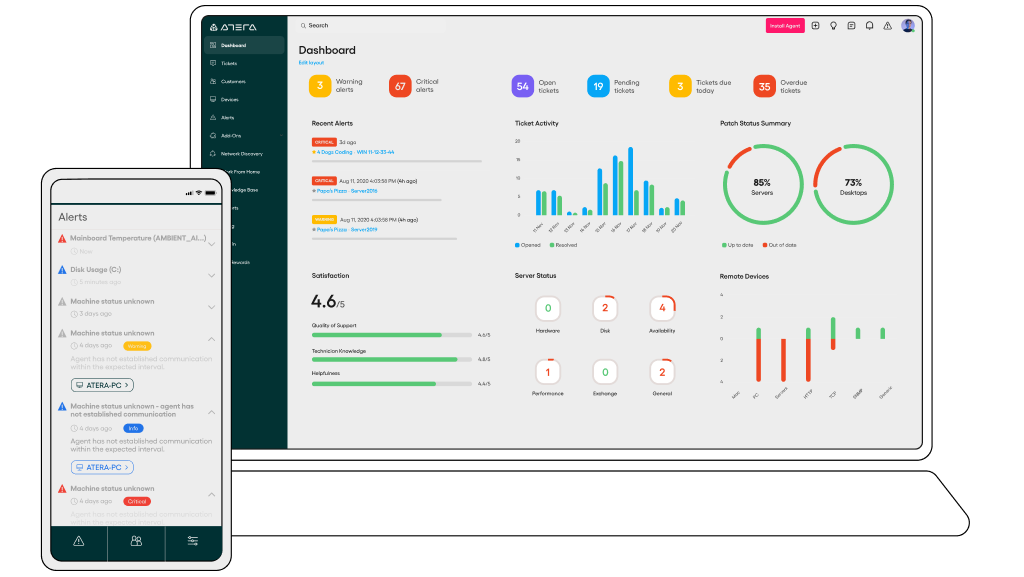
RMM software empowers IT professionals with a suite of tools designed to streamline endpoint management, enhance security, and optimize overall IT operations. These tools offer comprehensive functionality that simplifies complex tasks, reduces manual effort, and improves efficiency.
Remote Access and Control
Remote access and control capabilities allow IT professionals to connect to and manage endpoints remotely, regardless of their physical location. This functionality is crucial for:
- Troubleshooting issues: IT professionals can access and diagnose problems on remote devices without needing to physically visit the location.
- Installing software and updates: Remotely deploying software updates and patches ensures consistency and reduces downtime.
- Managing user accounts: RMM software enables remote account management, including password resets and user access control.
Endpoint Monitoring and Management
RMM software provides real-time monitoring of endpoints, enabling IT professionals to track key metrics and identify potential issues proactively. This functionality includes:
- Hardware monitoring: Tracking CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and other hardware parameters helps identify performance bottlenecks.
- Software inventory: RMM software can automatically scan endpoints to identify installed applications, ensuring compliance and security.
- System health monitoring: Monitoring system events, error logs, and other system-related information allows IT professionals to detect and address issues before they escalate.
Patching and Vulnerability Management
RMM software automates the process of patching and vulnerability management, ensuring endpoints are protected against known security threats.
- Automated patching: RMM software can automatically deploy security patches and updates to all endpoints, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability scanning: RMM software performs regular vulnerability scans to identify potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities in endpoints.
- Patch management policies: IT professionals can configure patch management policies to define the deployment schedule and prioritization of updates, ensuring a balance between security and operational efficiency.
Security and Threat Detection
RMM software incorporates security features to detect and mitigate threats, protecting endpoints from malicious attacks.
- Antivirus and malware protection: RMM software often integrates with antivirus solutions to provide real-time protection against malware.
- Firewall management: RMM software enables configuration and management of firewalls on endpoints, enhancing security by controlling network traffic.
- Intrusion detection and prevention: RMM software can monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, detecting and blocking potential intrusions.
Reporting and Analytics
RMM software provides comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, offering insights into IT operations and security posture.
- Performance metrics: RMM software generates reports on hardware usage, software inventory, and other performance metrics, allowing IT professionals to identify trends and optimize resource allocation.
- Security alerts: RMM software provides real-time alerts on security threats, vulnerabilities, and suspicious activity, enabling proactive threat management.
- Compliance reporting: RMM software helps organizations meet compliance requirements by generating reports on security posture and patch management activities.
RMM Deployment Models: Rmm Remote Management
Choosing the right deployment model for your RMM solution is crucial for optimizing its effectiveness and aligning it with your organization’s specific needs and infrastructure. Different deployment models offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, impacting factors like security, cost, scalability, and control.
On-Premises Deployment
On-premises deployment involves installing and managing the RMM server within your own data center or physical infrastructure. This model provides complete control over the RMM environment, allowing for customization and integration with existing systems.
- Pros:
- Enhanced security: On-premises deployment offers greater control over data security and compliance, as the RMM server is physically located within your organization’s infrastructure.
- Customization: You have complete control over the RMM environment, allowing for customization and integration with existing systems.
- Scalability: On-premises deployment can be scaled to accommodate growing needs, although this may require additional hardware and infrastructure investment.
- Cons:
- Higher upfront costs: On-premises deployment requires significant initial investment in hardware, software, and IT staff to manage the infrastructure.
- Increased maintenance overhead: Maintaining and updating the RMM server and its infrastructure can be time-consuming and require specialized expertise.
- Limited accessibility: Accessing the RMM server remotely may require additional security measures and VPN connections.
On-premises deployment is best suited for organizations with a strong IT infrastructure, a dedicated team to manage the RMM server, and a preference for greater control over their data and security. Examples of organizations that may opt for this model include financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies with stringent security requirements.
Cloud-Based Deployment
Cloud-based RMM solutions are hosted on a third-party cloud provider’s infrastructure, offering a subscription-based model with pay-as-you-go pricing. This model eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and provides accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Pros:
- Lower upfront costs: Cloud-based deployment eliminates the need for significant upfront investment in hardware and software, making it a more cost-effective option for smaller organizations.
- Reduced maintenance overhead: Cloud providers handle the infrastructure maintenance, updates, and security, freeing up your IT team to focus on other tasks.
- Improved accessibility: Cloud-based RMM solutions are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making it easier for remote teams to manage devices.
- Scalability: Cloud-based solutions offer high scalability, allowing you to easily adjust your resources based on your needs.
- Cons:
- Limited control: You have less control over the RMM environment compared to on-premises deployment, relying on the cloud provider for security and updates.
- Potential security concerns: Data security and compliance are reliant on the cloud provider’s security measures, which may not always meet the specific needs of all organizations.
- Internet dependency: Access to the RMM server requires a stable internet connection, which can be a concern in areas with unreliable internet access.
Cloud-based deployment is a popular choice for organizations seeking a cost-effective and scalable solution with minimal maintenance overhead. This model is particularly well-suited for businesses with geographically dispersed teams, limited IT resources, or a preference for outsourcing infrastructure management. Examples include startups, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), and organizations with remote workforces.
Hybrid Deployment
Hybrid deployment combines elements of both on-premises and cloud-based deployment models, offering a balance between control and flexibility. In this model, certain components of the RMM solution are hosted on-premises, while others are managed in the cloud.
- Pros:
- Increased flexibility: Hybrid deployment allows you to choose the best deployment model for different components of your RMM solution, maximizing control and cost-effectiveness.
- Improved security: You can maintain control over sensitive data and critical systems while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud services.
- Enhanced scalability: Hybrid deployment offers the flexibility to scale on-premises resources as needed while leveraging the scalability of cloud services.
- Cons:
- Increased complexity: Managing a hybrid deployment requires coordinating between on-premises and cloud environments, potentially adding complexity to your IT operations.
- Potential for compatibility issues: Integrating on-premises and cloud components may require careful planning to ensure compatibility and seamless operation.
Hybrid deployment is ideal for organizations seeking a balanced approach that offers the control of on-premises deployment with the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of cloud solutions. This model is suitable for organizations with a mix of on-premises and cloud infrastructure, or those with specific security requirements that need to be addressed locally while leveraging the benefits of cloud services. Examples include large enterprises with complex IT environments, organizations with a mix of on-premises and cloud applications, and those seeking to migrate to the cloud gradually.
RMM Use Cases
RMM solutions offer a wide range of benefits for organizations of all sizes. By automating routine tasks, streamlining workflows, and providing real-time insights, RMM empowers IT teams to improve efficiency, enhance security, and deliver exceptional service. Let’s explore some real-world examples of how RMM is used to achieve these goals.
Improving IT Efficiency and Productivity
RMM significantly improves IT efficiency and productivity by automating repetitive tasks, simplifying patch management, and providing centralized control over devices.
- Automated Patch Management: RMM automates the process of identifying and installing software updates across multiple devices, eliminating the need for manual intervention. This ensures that systems are always up-to-date with the latest security patches, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and downtime.
- Remote Device Management: RMM enables IT teams to manage and troubleshoot devices remotely, regardless of location. This eliminates the need for on-site visits, saving time and resources. For example, an IT administrator can remotely access a user’s computer to fix a software issue or install a new application, without having to physically visit the user’s office.
- Automated Scripting and Task Scheduling: RMM allows IT teams to create and schedule automated scripts to perform routine tasks, such as backing up data, running system checks, or restarting services. This frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Enhancing Security Posture and Compliance
RMM strengthens security posture and ensures compliance with industry regulations by providing centralized control over devices, enabling proactive threat detection, and automating security tasks.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Remediation: RMM tools can scan devices for vulnerabilities and automatically remediate them, reducing the risk of security breaches. This helps organizations meet compliance requirements and protect sensitive data.
- Endpoint Security and Monitoring: RMM solutions provide real-time monitoring of endpoint devices, allowing IT teams to identify and respond to security threats quickly. This includes features like malware detection, intrusion prevention, and data loss prevention.
- Centralized Policy Enforcement: RMM enables organizations to enforce security policies across all devices, ensuring that users adhere to best practices and minimize security risks. For instance, an organization can use RMM to enforce password complexity requirements, disable unauthorized applications, and restrict access to sensitive data.
Reducing Downtime and Resolving Issues Proactively
RMM minimizes downtime and proactively resolves issues by enabling remote monitoring, automated alerts, and proactive maintenance.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: RMM tools provide real-time monitoring of system performance, hardware health, and network connectivity. This allows IT teams to identify and address potential issues before they impact users. For example, if a server’s CPU utilization is consistently high, RMM can send an alert to the IT team, allowing them to investigate and resolve the issue before it leads to performance degradation.
- Proactive Maintenance and Patching: RMM automates routine maintenance tasks, such as software updates, antivirus scans, and system checks. This ensures that systems are running smoothly and reduces the likelihood of unexpected downtime.
- Remote Troubleshooting and Support: RMM enables IT teams to remotely troubleshoot and resolve issues, reducing the need for on-site visits and minimizing downtime. For example, if a user is experiencing a software issue, an IT administrator can remotely access their computer to diagnose and fix the problem.
Optimizing IT Infrastructure and Resource Allocation
RMM optimizes IT infrastructure and resource allocation by providing insights into device utilization, network performance, and application usage.
- Performance Monitoring and Optimization: RMM tools provide detailed performance metrics, allowing IT teams to identify bottlenecks and optimize system performance. This helps organizations ensure that their IT infrastructure is meeting their business needs and that resources are being used efficiently.
- Capacity Planning and Resource Allocation: RMM provides insights into device utilization, network bandwidth usage, and application performance, enabling IT teams to make informed decisions about capacity planning and resource allocation. This helps organizations avoid overspending on hardware and software and ensures that they have the resources they need to support their business operations.
- Software License Management: RMM solutions can help organizations track software licenses, ensuring that they are using the right licenses for their needs and avoiding compliance issues.
Choosing the Right RMM Solution
Selecting the right RMM solution is crucial for any organization looking to streamline IT operations, improve security, and enhance efficiency. With numerous options available, making an informed decision requires careful consideration of various factors that align with your specific needs and goals.
Scalability and Flexibility
The ability to scale and adapt to evolving needs is a critical aspect of any RMM solution. Consider the current and projected size of your IT infrastructure, the number of devices you need to manage, and the potential for growth. Look for solutions that offer:
- Scalable architecture: The RMM solution should be able to handle an increasing number of devices and users without compromising performance.
- Flexible deployment options: The solution should be compatible with your existing IT infrastructure and offer flexibility in terms of deployment models, such as on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid.
- Customizable features: The RMM solution should allow you to tailor features and functionalities to meet your specific requirements.
Cost and Pricing Models
Cost is a significant factor in any technology investment. RMM solutions offer different pricing models, and it’s essential to evaluate which best suits your budget and requirements. Consider:
- Subscription-based pricing: This model typically involves a monthly or annual fee based on the number of devices or users managed.
- Per-device pricing: This model charges a fee for each device managed, which can be a cost-effective option for organizations with a large number of devices.
- Tiered pricing: This model offers different tiers of service with varying features and pricing based on the level of support required.
Feature Set and Functionality
The features and functionalities offered by an RMM solution should align with your specific needs and goals. Consider the following:
- Remote access and control: The solution should provide secure remote access to devices for troubleshooting, software installation, and other tasks.
- Patch management: The solution should automate patch management to ensure systems are protected from vulnerabilities.
- Security monitoring and alerting: The solution should monitor for security threats and provide alerts to address potential issues promptly.
- Endpoint management: The solution should enable you to manage software, hardware, and other aspects of endpoints from a central location.
- Reporting and analytics: The solution should provide comprehensive reports and analytics to track key performance indicators and identify areas for improvement.
User Interface and Ease of Use
A user-friendly interface is crucial for any RMM solution, as it ensures that IT teams can easily navigate and utilize the platform. Consider:
- Intuitive interface: The interface should be easy to understand and use, with clear menus, icons, and navigation options.
- Customization options: The solution should allow users to customize the interface to suit their preferences and workflows.
- Mobile accessibility: The solution should offer mobile access for managing devices and responding to alerts on the go.
Vendor Support and Reputation
Choosing a vendor with a strong reputation for reliability, responsiveness, and customer support is crucial. Consider:
- Customer support: The vendor should offer responsive and reliable customer support through various channels, such as phone, email, and chat.
- Training and documentation: The vendor should provide adequate training and documentation to help users learn and utilize the solution effectively.
- Industry reputation: The vendor should have a positive reputation in the industry for delivering high-quality products and services.
RMM Security Considerations
RMM solutions offer significant benefits for IT management, but they also introduce security risks that need careful consideration. This section explores the security implications of RMM solutions and Artikels best practices for securing RMM deployments.
Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are paramount concerns in any IT management solution. RMM solutions often collect and store sensitive information about devices, users, and networks. This data must be protected from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
- Data Encryption: All data transmitted between the RMM server and agents, as well as data stored on the RMM server, should be encrypted using strong algorithms like AES-256. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable.
- Access Control: Implement robust access control mechanisms to restrict access to RMM data based on user roles and permissions. This helps prevent unauthorized personnel from accessing sensitive information.
- Data Retention Policies: Establish clear data retention policies that define how long data is stored and when it should be deleted. This helps minimize the risk of data breaches and comply with data privacy regulations.
Access Control and Authorization, Rmm remote management
RMM solutions provide remote access to managed devices, which can be a security risk if not properly controlled. Unauthorized access can lead to data theft, malware infection, or system compromise.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all RMM administrator accounts. This requires users to provide two or more authentication factors, such as a password and a one-time code, to gain access. MFA significantly strengthens account security.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to define specific permissions for different user roles within the RMM solution. This ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their tasks.
- Session Monitoring: Monitor all RMM sessions to detect suspicious activity. This includes logging user actions, session duration, and any unusual patterns. Real-time monitoring helps identify and mitigate potential threats.
Vulnerability Management and Patching
RMM solutions can play a crucial role in vulnerability management and patching. They can automatically scan devices for vulnerabilities, identify missing patches, and apply updates. This helps reduce the risk of exploitation by attackers.
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan managed devices for known vulnerabilities using automated tools. This helps identify and prioritize vulnerabilities that need immediate attention.
- Patch Management: Implement automated patch management policies to ensure that devices are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches. This reduces the attack surface and minimizes the risk of exploitation.
- Vulnerability Remediation: Develop a process for quickly remediating vulnerabilities. This includes prioritizing vulnerabilities based on severity, applying patches, and verifying the effectiveness of the remediation efforts.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
RMM solutions must comply with relevant industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. These regulations impose specific requirements for data privacy, security, and compliance.
- Data Protection: Implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data in accordance with relevant regulations. This includes encryption, access control, and data retention policies.
- Data Subject Rights: Ensure that data subjects have the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict, and object to the processing of their personal data.
- Data Breach Notification: Implement a data breach notification process to promptly report any data breaches to affected individuals and relevant authorities.
RMM Trends and Innovations
The RMM landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the growing demand for more efficient and secure IT management solutions. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of RMM, promising to deliver even greater value to businesses.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming various industries, and RMM is no exception. These technologies are being incorporated into RMM solutions to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and enhance security.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered RMM tools can analyze historical data to predict potential device failures, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Automated Patching: AI can identify and prioritize critical security updates, automating the patching process and minimizing vulnerabilities.
- Threat Detection and Response: ML algorithms can detect suspicious activity and anomalies, alerting IT teams to potential threats in real-time.
Cloud-Native RMM Solutions
Cloud-native RMM solutions are becoming increasingly popular, offering several advantages over traditional on-premises solutions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based RMM platforms can easily scale to accommodate growing IT environments and adapt to changing business needs.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Cloud solutions enable remote access and collaboration, allowing IT teams to manage devices from anywhere, anytime.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based RMM solutions often have lower upfront costs and eliminate the need for on-premises infrastructure.
Integration with Automation and Orchestration Tools
Integrating RMM solutions with automation and orchestration tools can significantly streamline IT operations.
- Automated Workflows: RMM platforms can be integrated with automation tools to automate repetitive tasks, such as software deployments, user provisioning, and system updates.
- Simplified Incident Response: Orchestration tools can automate incident response processes, reducing the time it takes to resolve issues and minimize downtime.
- Improved Efficiency: By automating tasks and processes, IT teams can focus on more strategic initiatives, improving overall efficiency and productivity.
Focus on Security and Compliance
As cyber threats continue to evolve, security and compliance are becoming paramount considerations for businesses.
- Enhanced Security Features: RMM solutions are incorporating advanced security features, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR), vulnerability scanning, and data loss prevention (DLP).
- Compliance Automation: RMM platforms can help organizations automate compliance tasks, ensuring adherence to industry regulations and standards.
- Proactive Security Posture: RMM solutions provide real-time visibility into security posture, enabling proactive threat mitigation and incident response.
Last Point
RMM remote management has emerged as an indispensable tool for modern IT operations, offering a comprehensive suite of features that empower organizations to achieve greater efficiency, security, and productivity. As technology continues to evolve, RMM solutions will continue to adapt and innovate, offering even more advanced capabilities to streamline IT operations and drive business success.
RMM remote management software streamlines IT operations by allowing technicians to manage devices remotely. This can include tasks like software updates, security patching, and troubleshooting, which can be done efficiently without needing to be physically present at the device.
For example, if you need to download multiple videos from YouTube for a training session, you can use a tool like the youtube multi downloader to automate the process. RMM solutions can then be used to distribute these videos to all the devices that need them, ensuring everyone has access to the necessary information.