RMM for internal IT departments sets the stage for a more efficient and secure IT landscape. This powerful technology empowers IT teams to proactively manage, monitor, and protect their organization’s assets, all from a centralized platform.
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where patching vulnerabilities, deploying software updates, and resolving incidents are streamlined and automated. This is the promise of RMM, which offers a comprehensive suite of tools to simplify complex IT tasks, enhance security posture, and ultimately improve the overall efficiency of IT operations.
Benefits of Implementing RMM
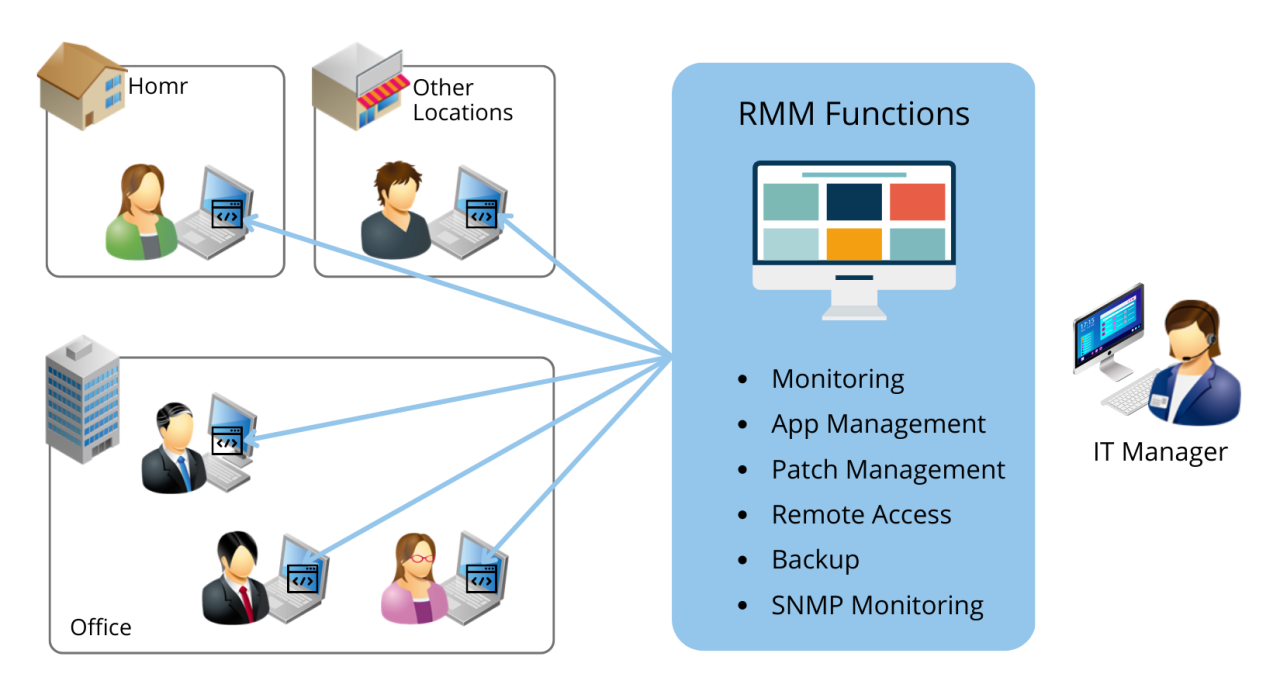
Implementing a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solution can significantly enhance your internal IT department’s efficiency, security, and overall effectiveness. By providing centralized control, automated tasks, and real-time insights, RMM empowers IT teams to proactively manage IT assets, mitigate risks, and optimize operations.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity, Rmm for internal it department
RMM streamlines IT operations by automating repetitive tasks, such as software updates, patch management, and system backups. This frees up valuable time for IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives, such as troubleshooting complex issues, developing new solutions, and collaborating with other departments.
“By automating routine tasks, we were able to reduce our IT staff’s workload by 20%, allowing them to focus on more complex projects and strategic initiatives,” said the IT Director of a large manufacturing company.
Enhanced Security Posture and Threat Management
RMM tools provide comprehensive security monitoring and threat detection capabilities, enabling proactive identification and mitigation of potential vulnerabilities. By continuously scanning for security threats, implementing security policies, and monitoring user activity, RMM helps organizations stay ahead of cyberattacks and protect sensitive data.
“Our RMM solution has been instrumental in detecting and responding to security threats in real-time, significantly reducing our risk of data breaches and cyberattacks,” shared the IT Manager of a financial services firm.
Key Features and Functionality of RMM Solutions
RMM solutions are equipped with a comprehensive suite of features that streamline IT operations and enhance security posture. These features work in synergy to provide a holistic approach to managing IT infrastructure, ultimately improving efficiency and reducing risk.
Remote Access and Control
Remote access and control is a fundamental feature of RMM solutions, enabling IT professionals to manage and troubleshoot endpoints remotely. This capability eliminates the need for physical presence at the device, saving time and resources.
- Remote desktop access allows IT personnel to view and interact with the endpoint’s desktop as if they were physically present. This enables them to diagnose and resolve issues, install software, or perform other tasks without needing to travel to the device’s location.
- Remote command execution enables IT professionals to execute commands on the endpoint, such as restarting services, running scripts, or installing software. This eliminates the need for manual intervention and allows for automated tasks.
- Remote file transfer enables the transfer of files between the endpoint and the IT professional’s computer. This is useful for transferring log files, configuration files, or software packages.
Patch Management and Software Updates
Patch management and software updates are crucial for maintaining the security and stability of endpoints. RMM solutions automate these processes, ensuring that all devices are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates.
- Automatic patch scanning identifies missing patches and updates on endpoints.
- Automated patch deployment applies patches and updates to endpoints without manual intervention.
- Patch scheduling allows IT professionals to schedule patch deployments during off-peak hours to minimize disruption to users.
Endpoint Security and Vulnerability Scanning
Endpoint security and vulnerability scanning are essential for protecting endpoints from malware and other threats. RMM solutions provide robust security features that help organizations identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Antivirus and anti-malware protection prevents malware from infecting endpoints.
- Vulnerability scanning identifies security weaknesses in endpoints and software.
- Firewall management controls network traffic to and from endpoints.
- Intrusion detection and prevention detects and blocks malicious activity.
System Monitoring and Performance Analysis
System monitoring and performance analysis provide valuable insights into the health and performance of endpoints. RMM solutions offer comprehensive monitoring capabilities that enable IT professionals to identify and resolve performance issues before they impact users.
- Real-time system monitoring tracks key performance indicators (KPIs), such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and disk space.
- Performance analysis identifies trends and patterns in endpoint performance, helping IT professionals identify potential bottlenecks and performance issues.
- Alerting and notifications notify IT professionals of critical system events, such as hardware failures or software errors.
Asset Inventory and Management
Asset inventory and management are essential for tracking and managing all IT assets within an organization. RMM solutions provide comprehensive asset management capabilities, enabling IT professionals to maintain an accurate inventory of all devices and software.
- Automatic asset discovery identifies all devices and software on the network.
- Asset tracking provides a central repository for information about each asset, including hardware specifications, software licenses, and maintenance contracts.
- Asset reporting generates reports on asset utilization, software licenses, and other key metrics.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into the overall health and performance of IT infrastructure. RMM solutions generate comprehensive reports and analytics that enable IT professionals to identify trends, make informed decisions, and improve efficiency.
- Customizable reports allow IT professionals to generate reports on specific areas of interest.
- Data visualization presents data in easy-to-understand charts and graphs.
- Trend analysis identifies patterns and trends in IT data, helping IT professionals to predict future needs and make proactive decisions.
Ticketing and Incident Management
Ticketing and incident management streamline the process of resolving IT issues. RMM solutions provide integrated ticketing systems that allow users to report issues and track their progress.
- Ticket submission enables users to report IT issues through a self-service portal.
- Ticket assignment automatically routes tickets to the appropriate IT personnel.
- Ticket tracking provides a centralized view of all open tickets and their status.
- Incident management automates the process of responding to and resolving incidents.
Choosing the Right RMM Solution
Selecting the optimal RMM solution for your IT department is crucial for ensuring efficient and effective management of your technology infrastructure. This involves carefully considering various factors that align with your specific needs and objectives.
Scalability and Flexibility
The ability of an RMM solution to adapt to your evolving IT environment is paramount. Scalability refers to the solution’s capacity to handle an increasing number of devices and users without compromising performance. Flexibility, on the other hand, emphasizes the solution’s ability to accommodate diverse IT configurations and workflows. Consider the following aspects:
- Growth potential: Ensure the RMM solution can scale to accommodate future growth in your IT infrastructure, including the addition of new devices, users, and applications.
- Customization options: Look for solutions that offer customizable policies, scripts, and reporting features to tailor the RMM solution to your specific needs and workflows.
- Cloud-based vs. On-premise: Cloud-based solutions typically offer greater scalability and flexibility due to their ability to dynamically adjust resources based on demand. On-premise solutions may require more upfront investment and ongoing maintenance but offer greater control over data and security.
Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure
Seamless integration with your existing IT infrastructure is essential for a smooth transition and optimal performance. This involves considering compatibility with your existing systems, such as:
- Operating systems: The RMM solution should support the operating systems used by your devices, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile platforms.
- Active Directory: Integration with Active Directory enables centralized user management and simplifies device onboarding.
- Monitoring tools: Compatibility with existing monitoring tools allows for consolidated reporting and centralized management of your IT environment.
- Security solutions: Integration with security solutions like antivirus and endpoint detection and response (EDR) enhances your overall security posture.
Ease of Use and User Interface
An intuitive and user-friendly interface is crucial for maximizing adoption and ensuring that your IT team can effectively utilize the RMM solution. Consider:
- User interface design: The interface should be clear, concise, and easy to navigate, even for users with limited technical expertise.
- Training and documentation: Adequate training materials and documentation should be available to help users understand the solution’s features and functionality.
- Mobile accessibility: The ability to manage devices and tasks from mobile devices enhances flexibility and responsiveness.
Pricing and Licensing Models
The cost of an RMM solution is a significant factor, and it’s essential to choose a solution that fits your budget and aligns with your licensing needs.
- Subscription vs. Perpetual Licensing: Subscription-based models offer predictable monthly costs and access to the latest features and updates. Perpetual licenses involve a one-time upfront cost but may require additional fees for updates and support.
- Pricing per device: Consider the pricing structure based on the number of devices managed. Some solutions offer tiered pricing based on device count.
- Additional features: Some solutions offer additional features, such as remote control, patch management, and asset management, at an additional cost.
Customer Support and Technical Assistance
Reliable customer support and technical assistance are crucial for resolving issues and maximizing the value of your RMM solution. Consider:
- Response time: Ensure the vendor offers prompt and responsive support, ideally 24/7.
- Support channels: Multiple support channels, such as phone, email, and live chat, provide flexibility and convenience.
- Knowledge base and documentation: Comprehensive knowledge base articles and documentation can help resolve common issues independently.
Implementing and Managing RMM

Successfully implementing and managing an RMM solution requires a systematic approach, ensuring a smooth transition and maximized benefits for your IT department. This section delves into the essential steps, emphasizing planning, configuration, and user training to optimize your RMM deployment.
Planning for RMM Implementation
Effective planning is crucial for a successful RMM implementation. It sets the stage for a seamless transition and maximizes the benefits of the chosen solution. This includes defining clear objectives, identifying key stakeholders, and conducting a thorough assessment of your existing IT infrastructure.
- Define clear objectives: Establish specific goals for implementing RMM, such as improving endpoint security, streamlining patch management, or automating routine tasks.
- Identify key stakeholders: Involve relevant IT personnel, including administrators, technicians, and help desk staff, in the planning process to ensure buy-in and address potential concerns.
- Assess existing infrastructure: Analyze your current IT environment, including hardware, software, and network configuration, to determine compatibility and identify potential integration challenges.
Configuring the RMM Solution
Once you’ve chosen an RMM solution, the next step is configuration. This involves setting up the platform, defining policies, and integrating with existing systems. A well-configured RMM solution is key to maximizing its effectiveness and achieving your desired outcomes.
- Install and configure the RMM agent: Deploy the RMM agent on all managed endpoints, ensuring proper installation and configuration to enable remote access and management capabilities.
- Define security policies: Establish comprehensive security policies, including password complexity, software restrictions, and endpoint hardening measures, to protect your systems and data.
- Integrate with existing systems: Connect the RMM solution with other IT tools and systems, such as ticketing systems, Active Directory, and monitoring platforms, to streamline workflows and improve data visibility.
User Training and Onboarding
User training is critical to ensure successful adoption and maximize the value of your RMM solution. Providing comprehensive training to IT staff and end-users empowers them to effectively use the platform and leverage its features.
- Develop a training curriculum: Create a structured training program that covers essential aspects of the RMM solution, including agent installation, policy management, and reporting features.
- Provide hands-on training: Offer practical training sessions that allow users to work with the RMM platform and apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Offer ongoing support: Establish a support system, such as a dedicated help desk or knowledge base, to assist users with any questions or challenges they may encounter.
Managing and Optimizing RMM Operations
Ongoing management and optimization are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of your RMM solution. This involves monitoring performance, analyzing data, and making adjustments to improve efficiency and security.
- Monitor RMM performance: Regularly track key metrics, such as agent status, patch deployment rates, and security alerts, to identify potential issues and ensure optimal operation.
- Analyze RMM data: Utilize the reporting and analytics capabilities of the RMM solution to gain insights into system performance, security threats, and user behavior.
- Optimize RMM configuration: Continuously evaluate and adjust RMM policies, settings, and integrations based on data analysis, security best practices, and evolving IT needs.
Future Trends in RMM: Rmm For Internal It Department
The RMM landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the changing demands of businesses. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of RMM, making it more powerful, efficient, and secure.
Integration with Cloud-Based Services and Platforms
The increasing adoption of cloud computing has led to a significant shift in how businesses manage their IT infrastructure. RMM solutions are increasingly integrating with cloud-based services and platforms to provide a seamless and unified management experience. This integration allows businesses to manage their on-premises and cloud-based resources from a single console, simplifying operations and improving efficiency.
- Cloud-based RMM platforms offer a centralized management console that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure. This provides flexibility and scalability for businesses of all sizes.
- Integration with cloud storage services, such as Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive, allows for centralized data storage and backup, ensuring data security and accessibility.
- Integration with cloud-based communication platforms, such as Slack and Microsoft Teams, enables real-time collaboration and communication between IT teams and end-users.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Automation and Optimization
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming the RMM landscape by automating tasks and optimizing IT operations. AI-powered RMM solutions can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential issues, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- AI-driven automation can automate repetitive tasks, such as software updates, patch management, and endpoint security checks, freeing up IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- ML algorithms can analyze historical data to identify trends and predict future issues, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime. For example, ML algorithms can predict when a server is likely to fail based on its performance history, allowing IT teams to take preventative measures.
- AI-powered threat intelligence can identify and respond to emerging threats in real-time, enhancing security posture and minimizing the risk of cyberattacks.
Enhanced Security Features and Threat Intelligence
Cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it crucial for RMM solutions to provide robust security features and threat intelligence. RMM solutions are incorporating advanced security features, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR), threat intelligence feeds, and vulnerability assessments, to protect businesses from evolving cyber threats.
- EDR solutions provide real-time monitoring and threat detection capabilities, enabling IT teams to quickly identify and respond to malicious activity on endpoints.
- Threat intelligence feeds provide insights into emerging threats and vulnerabilities, allowing IT teams to proactively mitigate risks and protect their systems.
- Vulnerability assessments identify security weaknesses in systems and applications, enabling IT teams to prioritize remediation efforts and strengthen their security posture.
Focus on User Experience and Ease of Use
Modern RMM solutions are focusing on providing a user-friendly experience for both IT professionals and end-users. Intuitive interfaces, comprehensive reporting, and mobile access are becoming essential features, making RMM solutions more accessible and user-friendly.
- Intuitive interfaces make it easy for IT professionals to navigate and manage their systems, reducing the learning curve and improving efficiency.
- Comprehensive reporting provides valuable insights into IT operations, enabling IT teams to track performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
- Mobile access allows IT professionals to manage their systems from anywhere, providing flexibility and enabling them to respond to issues quickly.
Last Word
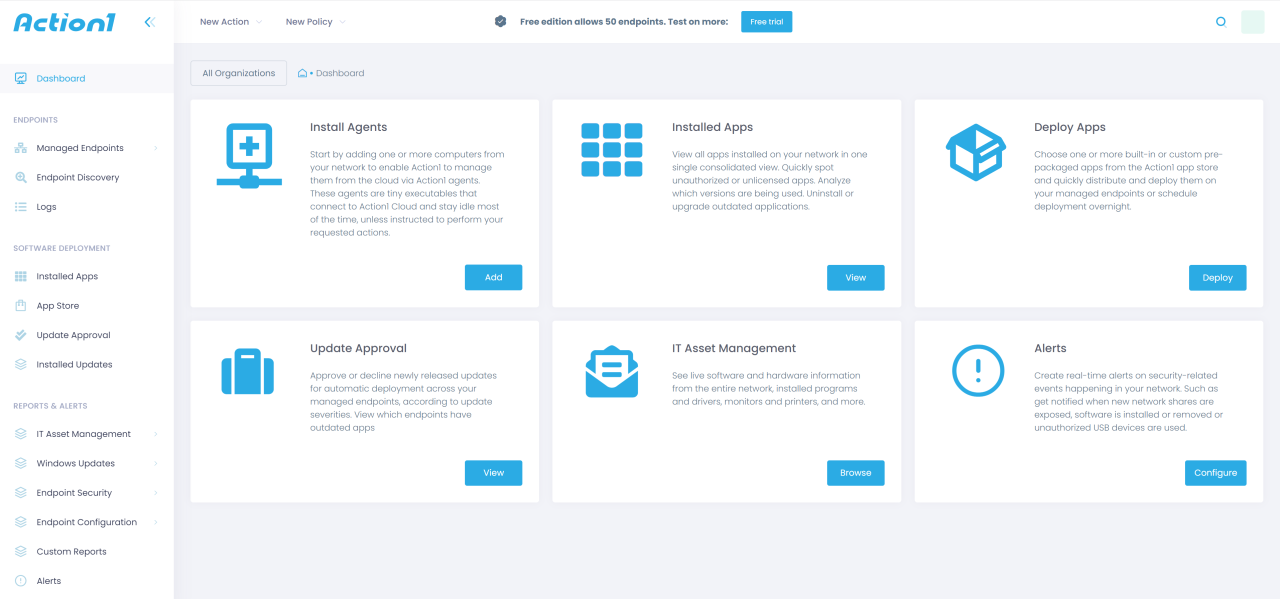
Implementing RMM is a strategic decision that empowers IT departments to elevate their capabilities and achieve tangible results. By embracing the power of automation, proactive monitoring, and robust security measures, organizations can confidently navigate the ever-evolving IT landscape, ensuring business continuity and optimal performance.
An RMM for an internal IT department can streamline processes and improve efficiency. The same benefits can be enjoyed by smaller businesses with the right tools, and a good starting point is to explore rmm for small business solutions.
This can help you choose a system that fits your specific needs and budget, regardless of your company size.
