Remote network monitoring software is an indispensable tool for businesses and organizations in today’s digital landscape. It empowers IT professionals to gain real-time visibility into network performance, security, and user experience, allowing them to proactively identify and address potential issues before they impact operations.
Table of Contents
By leveraging remote monitoring software, businesses can optimize network performance, enhance security posture, and ensure continuous availability, ultimately contributing to a more efficient and resilient IT infrastructure. This comprehensive guide explores the key features, benefits, and considerations of remote network monitoring software, providing insights into its implementation, security, and future trends.
Introduction to Remote Network Monitoring Software
Remote network monitoring software is a powerful tool that enables IT professionals to gain real-time visibility into the health and performance of their network infrastructure from any location. This software uses various methods, including agents, sensors, and protocols, to collect data about network devices, applications, and services. By analyzing this data, administrators can identify potential problems, troubleshoot issues, and proactively optimize network performance.
The significance of remote network monitoring in today’s digital landscape cannot be overstated. Businesses and organizations rely heavily on their networks to operate efficiently, and any downtime or performance degradation can have significant financial and operational consequences. With the rise of cloud computing, remote workforces, and mobile devices, the need for comprehensive and robust network monitoring solutions has become more critical than ever.
Benefits of Remote Network Monitoring Software
Remote network monitoring software offers a wide range of benefits for businesses and organizations, including:
- Improved Network Visibility: Remote monitoring software provides a centralized view of the entire network infrastructure, allowing administrators to monitor all devices, applications, and services in real time. This comprehensive visibility enables them to quickly identify and address potential problems before they impact users.
- Enhanced Network Performance: By analyzing network data, administrators can identify bottlenecks, optimize network resources, and proactively address performance issues. This leads to a more efficient and responsive network, improving user experience and productivity.
- Reduced Downtime: Proactive monitoring allows administrators to identify and resolve issues before they cause major disruptions. This significantly reduces downtime, minimizing the impact on business operations and user productivity.
- Increased Security: Remote network monitoring software can detect suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or malware infections. This enables administrators to respond quickly and effectively to security threats, protecting the network and sensitive data.
- Cost Savings: By proactively identifying and resolving issues, remote monitoring software can prevent costly downtime and network outages. It also helps optimize network resource utilization, reducing energy consumption and infrastructure costs.
Key Features of Remote Network Monitoring Software
Remote network monitoring software is an indispensable tool for organizations of all sizes, providing valuable insights into network health, performance, and security. These solutions empower IT teams to proactively identify and address potential issues before they escalate, ensuring optimal network uptime and user experience.
Real-time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring is a cornerstone of effective network management, providing continuous visibility into network activity and performance. This feature allows IT teams to track key metrics such as bandwidth utilization, device availability, and application performance in real-time.
For example, a network administrator can use real-time monitoring to identify a sudden spike in bandwidth usage, potentially indicating a denial-of-service (DoS) attack or a malfunctioning device.
Real-time monitoring empowers swift identification and resolution of network issues, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth network operations.
Types of Remote Network Monitoring Software
Remote network monitoring software comes in various forms, each catering to specific needs and functionalities. These tools can be broadly categorized based on their target audience and the aspects of the network they focus on.
Network Performance Monitoring Software
Network performance monitoring (NPM) software is designed to track and analyze the health and efficiency of network infrastructure. It helps identify bottlenecks, performance issues, and potential problems before they impact users.
- Real-time Network Performance Monitoring: NPM tools provide real-time insights into network performance metrics like bandwidth utilization, latency, packet loss, and jitter. This enables administrators to proactively identify and resolve issues before they escalate.
- Network Traffic Analysis: These tools analyze network traffic patterns, identifying potential security threats, bandwidth hogs, and application performance issues. They can also help optimize network configurations and capacity planning.
- Network Availability Monitoring: NPM tools ensure the uptime and availability of network devices and services. They monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and trigger alerts when outages or performance degradation occur.
Examples of popular network performance monitoring software include:
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor: This comprehensive solution offers real-time network performance monitoring, traffic analysis, and network capacity planning.
- Datadog: Datadog is a cloud-based monitoring platform that provides extensive network performance monitoring capabilities, including network traffic analysis and visualization.
- PRTG Network Monitor: PRTG is a versatile network monitoring tool that offers a wide range of sensors for monitoring various network components and applications.
Security Monitoring Software
Security monitoring software focuses on identifying and mitigating security threats within a network. It plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access, and ensuring network security.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS solutions monitor network traffic for malicious activity, identifying and blocking potential attacks. They can detect various threats, including malware, denial-of-service attacks, and unauthorized access attempts.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM tools collect and analyze security data from various sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and log files. They provide a centralized view of security events, enabling administrators to identify and respond to threats more effectively.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning tools identify security weaknesses in network devices, applications, and operating systems. They help prioritize vulnerabilities and provide guidance on remediation strategies.
Examples of popular security monitoring software include:
- Splunk: Splunk is a powerful SIEM platform that offers real-time security monitoring, threat detection, and incident response capabilities.
- AlienVault OSSIM: OSSIM is an open-source SIEM platform that provides comprehensive security monitoring, threat intelligence, and vulnerability management features.
- Qualys: Qualys is a leading provider of vulnerability management and compliance solutions. Its software offers automated vulnerability scanning, remediation guidance, and compliance reporting.
Application Monitoring Software
Application monitoring software focuses on the performance and availability of applications running on the network. It helps ensure applications are functioning properly and meet user expectations.
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM): APM tools track the performance of applications, identifying bottlenecks and performance issues that impact user experience. They provide insights into application code, database performance, and web server health.
- Application Availability Monitoring: This type of software ensures the uptime and availability of applications, monitoring key metrics like response times, error rates, and service outages. It alerts administrators to any issues that affect application performance.
- Application Log Monitoring: Application log monitoring tools analyze application logs to identify errors, exceptions, and other issues that may indicate problems. They provide valuable insights into application behavior and help troubleshoot performance issues.
Examples of popular application monitoring software include:
- New Relic: New Relic is a comprehensive APM platform that provides real-time application performance monitoring, error tracking, and user experience insights.
- Dynatrace: Dynatrace is an AI-powered APM solution that offers automated performance analysis, root cause identification, and proactive problem resolution.
- AppDynamics: AppDynamics is a cloud-based APM platform that provides deep insights into application performance, user experience, and business impact.
Benefits of Using Remote Network Monitoring Software
Remote network monitoring software empowers businesses to gain comprehensive visibility into their network infrastructure, enabling proactive issue detection, enhanced security, and improved user experience. It plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal network performance and minimizing downtime, ultimately contributing to business continuity and success.
Proactive Issue Detection and Reduced Downtime
Remote network monitoring software allows businesses to identify and address network issues before they impact users. By continuously monitoring network performance metrics, such as bandwidth usage, latency, and packet loss, the software can detect anomalies and alert administrators to potential problems. This proactive approach enables swift troubleshooting and resolution, preventing disruptions and minimizing downtime.
“A proactive approach to network monitoring can reduce downtime by up to 80%.” – Gartner
For instance, a retail company using remote network monitoring software detected a sudden spike in bandwidth usage at one of its stores. This early warning allowed the IT team to investigate the issue and identify a rogue device consuming excessive bandwidth. By isolating the device and addressing the problem, the company avoided a network outage that could have disrupted customer service and sales.
Enhanced Security Posture
Remote network monitoring software plays a vital role in strengthening network security by providing real-time visibility into potential threats and vulnerabilities. The software can monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, identify unauthorized access attempts, and detect malware infections. By proactively identifying and responding to security threats, businesses can minimize the risk of data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other cyber security incidents.
“Businesses that actively monitor their networks are 70% less likely to experience a data breach.” – Ponemon Institute
For example, a financial institution using remote network monitoring software detected a suspicious login attempt from an unknown location. The software immediately alerted the security team, who investigated the incident and blocked the unauthorized access. This proactive response prevented a potential data breach and protected sensitive customer information.
Improved User Experience, Remote network monitoring software
Remote network monitoring software contributes to a better user experience by ensuring consistent network performance and minimizing disruptions. By monitoring network performance metrics, the software can identify and address issues that impact user productivity, such as slow network speeds, latency, and application outages. This proactive approach ensures that users have a seamless and reliable network experience, enhancing their productivity and satisfaction.
“Businesses that prioritize user experience through network monitoring see a 20% increase in employee productivity.” – Forrester Research
For example, a software development company using remote network monitoring software detected a slow network connection impacting its developers. The software alerted the IT team, who investigated the issue and identified a congested network switch. By addressing the bottleneck, the company restored network performance and improved the developer’s productivity.
Considerations for Choosing Remote Network Monitoring Software
Choosing the right remote network monitoring software is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation and security of your network. With a vast array of options available, it’s essential to carefully consider your specific needs and requirements before making a decision.
Evaluating Features
The features offered by remote network monitoring software play a vital role in its effectiveness.
- Real-time monitoring: This feature allows you to track network performance and identify issues as they occur, enabling proactive problem resolution.
- Performance metrics: The software should provide comprehensive performance metrics, such as bandwidth utilization, latency, and packet loss, to help you pinpoint performance bottlenecks.
- Alerting and notifications: Timely alerts and notifications are essential for prompt responses to critical network events. The software should offer customizable alert thresholds and notification methods.
- Reporting and analysis: Robust reporting and analysis capabilities allow you to gain insights into network trends, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions.
- Security monitoring: Security features, such as intrusion detection and prevention, are crucial for protecting your network from threats.
- Device and application monitoring: The software should be able to monitor individual devices and applications, providing detailed insights into their performance and resource utilization.
Security Considerations for Remote Network Monitoring
Remote network monitoring is essential for maintaining the health and security of your network, but it also introduces security risks that must be carefully addressed. Remote access and data collection can create vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit.
Securing Remote Access
Securing remote access is crucial for protecting your network from unauthorized access. Remote monitoring tools often rely on protocols like SSH or VPNs to establish secure connections.
- Use Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security by requiring multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, one-time codes, or biometric authentication. This makes it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to your monitoring system.
- Restrict Access: Limit access to the monitoring system to only authorized personnel. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to grant specific permissions based on user roles and responsibilities. This ensures that individuals only have access to the information and functionality they need to perform their duties.
- Secure Credentials: Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts associated with the remote monitoring system. Avoid using default passwords and change passwords regularly. Store passwords securely using password management tools or a dedicated password vault. Consider implementing password complexity requirements, such as a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep your monitoring software and operating systems updated with the latest security patches. These updates often include fixes for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Ensure that automatic updates are enabled to minimize the risk of outdated software.
Protecting Sensitive Data
Data collected by remote monitoring systems can include sensitive information about your network, devices, and users. It’s crucial to protect this data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data in transit and at rest. Encrypt data while it’s being transmitted between your network and the monitoring system using secure protocols like TLS/SSL. Additionally, encrypt data stored on the monitoring system’s servers or databases to prevent unauthorized access. Implement strong encryption algorithms and regularly rotate encryption keys.
- Access Control: Restrict access to sensitive data within the monitoring system. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to specific data. For example, you might limit access to network traffic logs to security analysts while providing administrators with broader access to configuration settings.
- Data Retention Policies: Establish data retention policies to determine how long data is stored and when it should be deleted. Regularly review and update these policies to ensure they align with your organization’s security requirements and legal obligations. Deleting data that is no longer needed reduces the potential attack surface and minimizes the risk of data breaches.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in your remote monitoring system. These audits should include assessments of your network security, access controls, data encryption, and logging and monitoring practices.
Best Practices for Effective Remote Network Monitoring
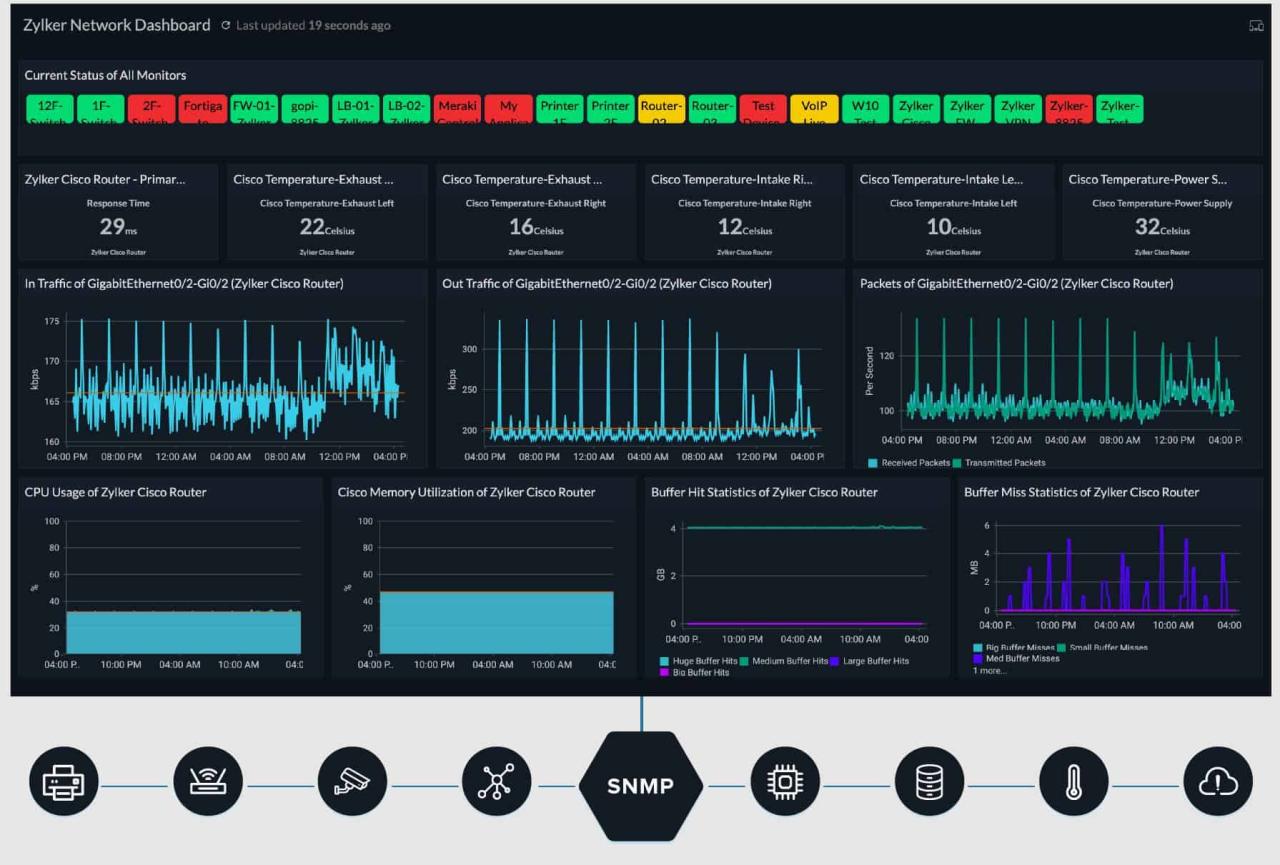
Remote network monitoring is an essential tool for ensuring the smooth operation of your IT infrastructure. By implementing best practices, you can maximize the effectiveness of your monitoring system and gain valuable insights into your network’s performance and security.
Establishing Monitoring Thresholds
Setting appropriate monitoring thresholds is crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Thresholds define the acceptable limits for various network metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and network bandwidth.
- Start with baseline monitoring: Establish a baseline for normal network activity by monitoring for a period of time under typical conditions. This baseline will serve as a reference point for identifying deviations from the norm.
- Define alert thresholds: Based on your baseline data, define alert thresholds for each monitored metric. These thresholds should be set at levels that indicate potential problems but avoid triggering false alerts.
- Consider specific requirements: Tailor thresholds to the specific requirements of your network and applications. For example, a web server might have higher CPU utilization thresholds than a file server.
- Regularly review and adjust thresholds: As your network evolves and changes, it is essential to regularly review and adjust monitoring thresholds to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
Interpreting Data and Responding to Alerts
Effective remote network monitoring involves more than just collecting data. It’s crucial to interpret the data and respond to alerts promptly and efficiently.
- Analyze trends and patterns: Look for trends and patterns in the collected data to identify recurring issues or potential problems. For example, a consistent increase in network latency might indicate a bottleneck or congestion.
- Prioritize alerts: Not all alerts are created equal. Prioritize alerts based on their severity and potential impact on your network and applications.
- Establish clear escalation procedures: Define clear escalation procedures for handling alerts, including who is responsible for addressing specific issues and the timeframes for responding.
- Document actions taken: Keep detailed records of all alerts, the actions taken to resolve them, and the outcomes. This documentation can help you identify recurring problems and improve your response time.
Optimizing Performance and Minimizing False Positives
Optimizing your monitoring system for performance and minimizing false positives are essential for ensuring accurate reporting and efficient troubleshooting.
- Monitor critical metrics: Focus on monitoring critical metrics that are most relevant to your network’s health and performance. This will reduce the amount of data you need to analyze and improve the efficiency of your monitoring system.
- Use filtering and correlation rules: Implement filtering and correlation rules to reduce the number of false positives. These rules can help identify and suppress alerts that are not truly indicative of a problem.
- Regularly test and refine your monitoring system: Regularly test and refine your monitoring system to ensure it is working effectively and identify areas for improvement.
- Consider using a combination of monitoring tools: Utilizing multiple monitoring tools can provide a more comprehensive view of your network and reduce the risk of missed issues.
Future Trends in Remote Network Monitoring
The landscape of remote network monitoring is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the growing demand for more sophisticated and efficient solutions. Emerging trends are shaping the future of this field, presenting exciting opportunities for organizations to enhance their network security, performance, and reliability.
The Impact of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is revolutionizing remote network monitoring by offering scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions. Cloud-based monitoring platforms enable organizations to access powerful monitoring tools and resources without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud platforms provide on-demand scalability, allowing organizations to easily adjust their monitoring capabilities based on their needs. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or fluctuating workloads.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based solutions often offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, reducing the need for substantial capital expenditures on hardware and software. This can significantly lower the overall cost of network monitoring.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Cloud platforms provide remote access to monitoring data and tools, enabling teams to manage and monitor networks from anywhere with an internet connection. This improves collaboration and responsiveness, particularly for geographically dispersed organizations.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming remote network monitoring by automating tasks, identifying anomalies, and predicting potential issues. These technologies enable organizations to gain deeper insights into network behavior, optimize performance, and proactively address security threats.
- Automated Anomaly Detection: AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of network data to identify unusual patterns and deviations from normal behavior. This enables early detection of security breaches, performance bottlenecks, or other issues that could impact network operations.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data and current network conditions, AI and ML can predict potential failures or performance degradations. This allows organizations to proactively address issues before they impact network availability or performance.
- Security Threat Detection: AI and ML are increasingly used to identify and mitigate cyber threats. These technologies can analyze network traffic patterns, identify suspicious activity, and detect malware or other malicious attacks.
Future Developments and Innovations
The future of remote network monitoring is characterized by ongoing innovation and the development of advanced technologies. Some key areas of focus include:
- Internet of Things (IoT) Monitoring: As the number of connected devices continues to grow, remote monitoring solutions will need to adapt to the unique challenges and opportunities presented by IoT networks. This includes monitoring the performance and security of IoT devices, managing data flows, and ensuring seamless integration with existing network infrastructure.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings data processing and analysis closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. This trend is expected to play a significant role in remote network monitoring, enabling faster response times and more localized insights.
- Enhanced User Experience: Future remote monitoring solutions will focus on providing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, enabling organizations to access critical network information and insights easily. This includes leveraging advanced visualization techniques, real-time dashboards, and personalized reporting tools.
Examples of Remote Network Monitoring Software
Remote network monitoring software comes in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and offering a unique set of features. This section explores some popular solutions, providing an overview of their capabilities, pricing, and target audience.
Popular Remote Network Monitoring Software Solutions
Remote network monitoring software solutions are diverse, offering features like performance monitoring, security analysis, and network troubleshooting. Here are some of the most widely used solutions:
| Software | Description | Key Features | Pricing | Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Datadog | Datadog is a cloud-based monitoring and observability platform that provides comprehensive insights into the performance and health of your applications, infrastructure, and networks. | Real-time monitoring, performance dashboards, alerts, anomaly detection, integrations with various tools, and comprehensive reporting. | Starts at $15 per host per month, with custom pricing options available. | https://www.datadog.com/ |
| SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM) | SolarWinds NPM is a powerful network monitoring solution that offers deep insights into network performance, traffic patterns, and potential issues. | Network discovery, performance analysis, bandwidth monitoring, alert management, network topology mapping, and reporting. | Starts at $2,995 for a 100-node license, with various pricing options available. | https://www.solarwinds.com/network-performance-monitor |
| ManageEngine OpManager | ManageEngine OpManager is a comprehensive network monitoring solution that offers a wide range of features for managing and monitoring network devices, applications, and servers. | Network discovery, performance monitoring, fault management, event correlation, customizable dashboards, and reporting. | Starts at $2,495 for a 25-node license, with various pricing options available. | https://www.manageengine.com/network-monitoring/opmanager.html |
| PRTG Network Monitor | PRTG Network Monitor is a versatile network monitoring solution that offers a user-friendly interface and a wide range of features for managing network devices and applications. | Network discovery, performance monitoring, traffic analysis, alerts, customizable dashboards, and reporting. | Starts at $1,600 for a 100-sensor license, with various pricing options available. | https://www.paessler.com/prtg |
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Remote network monitoring software has become an indispensable tool for businesses and organizations across various industries. By providing real-time insights into network performance, security, and user activity, these solutions enable proactive problem identification, mitigation of potential risks, and optimization of network infrastructure.
Real-World Examples of Remote Network Monitoring Software Implementation
Numerous businesses and organizations have successfully leveraged remote network monitoring software to achieve tangible benefits. Here are a few examples:
- Financial Institution: A large financial institution implemented a comprehensive remote network monitoring solution to ensure the security and availability of its critical financial systems. The software provided real-time alerts for suspicious activity, enabling security teams to promptly identify and respond to potential threats. This proactive approach significantly reduced the risk of data breaches and financial losses.
- Healthcare Provider: A healthcare provider deployed remote network monitoring software to optimize the performance of its medical imaging systems. The solution monitored network traffic and resource utilization, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing network configuration to improve image processing speed and reduce patient wait times.
- Educational Institution: An educational institution implemented remote network monitoring software to manage its growing network infrastructure. The software provided detailed insights into network performance, enabling IT administrators to identify and resolve issues proactively, ensuring seamless access to online resources for students and faculty.
Challenges Addressed and Positive Outcomes Achieved
Remote network monitoring software has proven to be effective in addressing a wide range of challenges faced by businesses and organizations. Some common challenges addressed include:
- Network Performance Optimization: Remote monitoring software helps identify and resolve network performance issues, such as slow connections, latency, and bandwidth bottlenecks. This leads to improved user experience, increased productivity, and reduced downtime.
- Security Threat Detection and Response: Remote monitoring software provides real-time visibility into network activity, enabling security teams to detect and respond to threats promptly. This proactive approach reduces the risk of data breaches, malware infections, and other security incidents.
- Resource Management and Optimization: Remote monitoring software provides insights into network resource utilization, enabling organizations to optimize resource allocation and ensure efficient utilization of network infrastructure. This can result in cost savings and improved network performance.
How Remote Monitoring Contributes to Improved Efficiency, Security, and Network Performance
Remote network monitoring software plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, security, and overall network performance:
- Improved Efficiency: Remote monitoring software automates network management tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Security: Remote monitoring software provides real-time insights into network activity, enabling security teams to detect and respond to threats promptly. This proactive approach strengthens network security and reduces the risk of data breaches.
- Optimized Network Performance: Remote monitoring software identifies and resolves network performance issues, ensuring optimal network performance and user experience. This leads to increased productivity, reduced downtime, and improved overall network efficiency.
Last Point
Remote network monitoring software is a powerful tool for achieving optimal network performance, security, and availability. By embracing this technology, businesses can gain valuable insights into their network infrastructure, enabling them to proactively identify and resolve issues, enhance security posture, and improve user experience. As technology continues to evolve, remote network monitoring will play an increasingly crucial role in ensuring a secure and efficient digital environment.
Remote network monitoring software can help you keep an eye on your system’s performance, but sometimes you need a more granular view. If you’re looking for a way to monitor your system’s temperature and fan speeds, you might consider downloading SpeedFan, a popular and powerful tool available at speedfan download.
While SpeedFan is focused on hardware monitoring, its insights can be integrated into your overall network monitoring strategy, providing a more complete picture of your system’s health.
