Remote monitoring and management (RMM) has revolutionized the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure. By providing a centralized platform for monitoring, managing, and securing devices remotely, RMM solutions empower organizations to optimize performance, reduce downtime, and enhance security.
Table of Contents
From small businesses to large enterprises, RMM solutions have become indispensable tools for streamlining IT operations and ensuring business continuity. By leveraging automation, remote access, and real-time monitoring capabilities, RMM solutions empower IT professionals to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact users or disrupt critical business processes.
What is Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM)?
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) is a powerful suite of tools that allows IT professionals to remotely manage and monitor computer systems and networks. It is a comprehensive solution that streamlines IT operations, improves security, and enhances productivity.
Core Functionalities of RMM
RMM solutions offer a wide range of functionalities, including:
- Remote access and control: RMM enables IT professionals to access and control devices remotely, allowing them to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other tasks without being physically present. This is especially beneficial for managing geographically dispersed teams or devices in remote locations.
- System monitoring: RMM solutions continuously monitor key system parameters such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network connectivity. They alert IT professionals to potential problems before they escalate into major issues, reducing downtime and preventing data loss.
- Patch management: RMM helps automate the process of applying software updates and security patches to devices. This ensures that systems are protected against vulnerabilities and ensures compliance with industry standards.
- Security management: RMM solutions include security features such as endpoint protection, malware detection, and firewall management. They help to protect devices from cyber threats and minimize the risk of data breaches.
- Reporting and analytics: RMM provides comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities that allow IT professionals to track system performance, identify trends, and optimize resource utilization. This data can be used to make informed decisions about IT infrastructure and resource allocation.
Benefits of Implementing RMM Solutions, Remote monitoring and management
RMM solutions offer numerous benefits to organizations of all sizes, including:
- Reduced IT costs: By automating tasks and streamlining IT operations, RMM solutions can significantly reduce IT staffing costs and improve efficiency. The ability to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact users also minimizes downtime and reduces the need for expensive emergency repairs.
- Improved security: RMM solutions offer robust security features that help to protect devices from cyber threats. Automated patch management and vulnerability scanning ensure that systems are kept up to date and secure, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
- Enhanced productivity: By providing IT professionals with the tools to quickly and efficiently resolve issues, RMM solutions can help to improve user productivity. Remote access and control capabilities allow IT professionals to provide support to users without having to physically visit their location.
- Increased compliance: RMM solutions can help organizations meet compliance requirements by automating tasks such as patch management and vulnerability scanning. This ensures that systems are compliant with industry standards and regulations.
- Improved visibility and control: RMM provides a centralized platform for managing and monitoring all devices in an organization. This gives IT professionals a comprehensive view of the IT infrastructure and allows them to make informed decisions about resource allocation and security.
How RMM Streamlines IT Operations and Reduces Downtime
RMM solutions streamline IT operations by automating tasks and providing a centralized platform for managing and monitoring devices. This reduces the workload on IT professionals and allows them to focus on strategic initiatives. By proactively identifying and resolving issues before they impact users, RMM solutions also minimize downtime and ensure business continuity.
“RMM solutions can help organizations save time and money by automating tasks, improving security, and reducing downtime.”
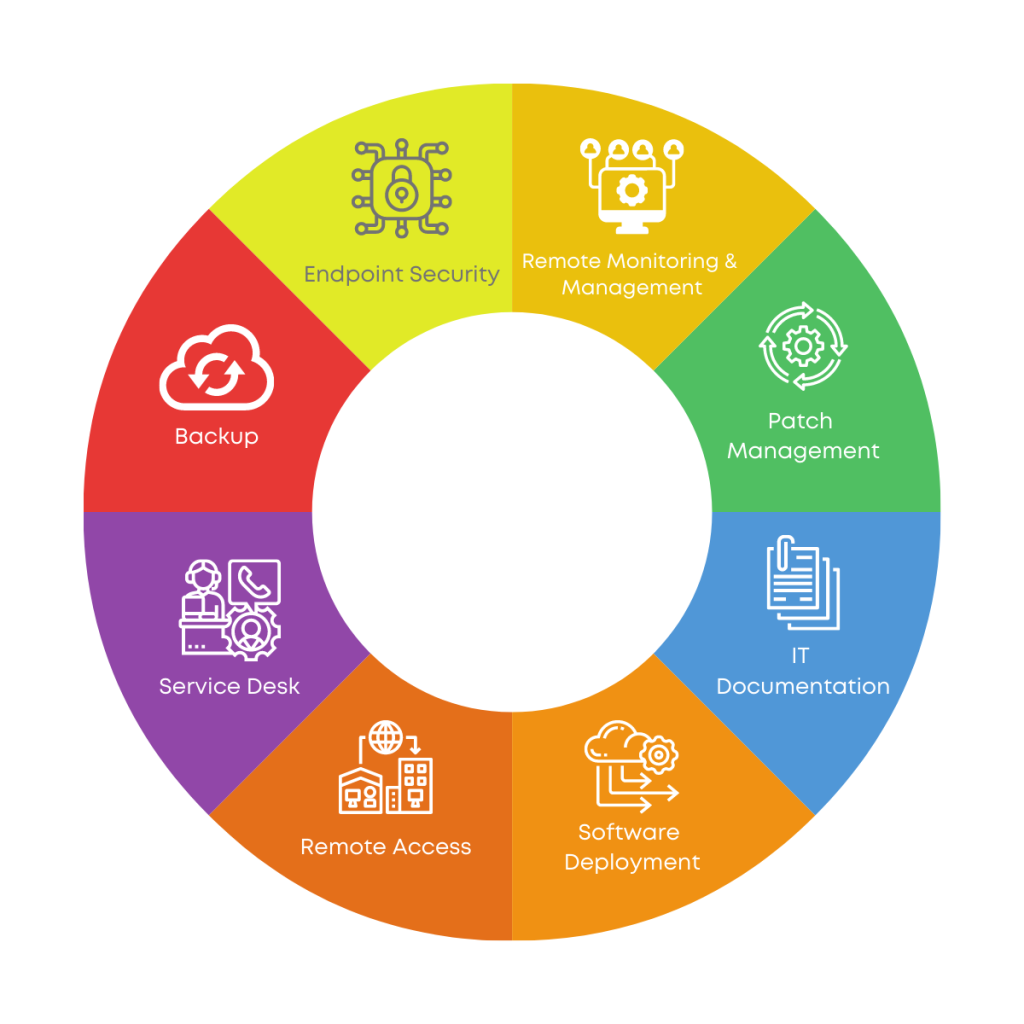
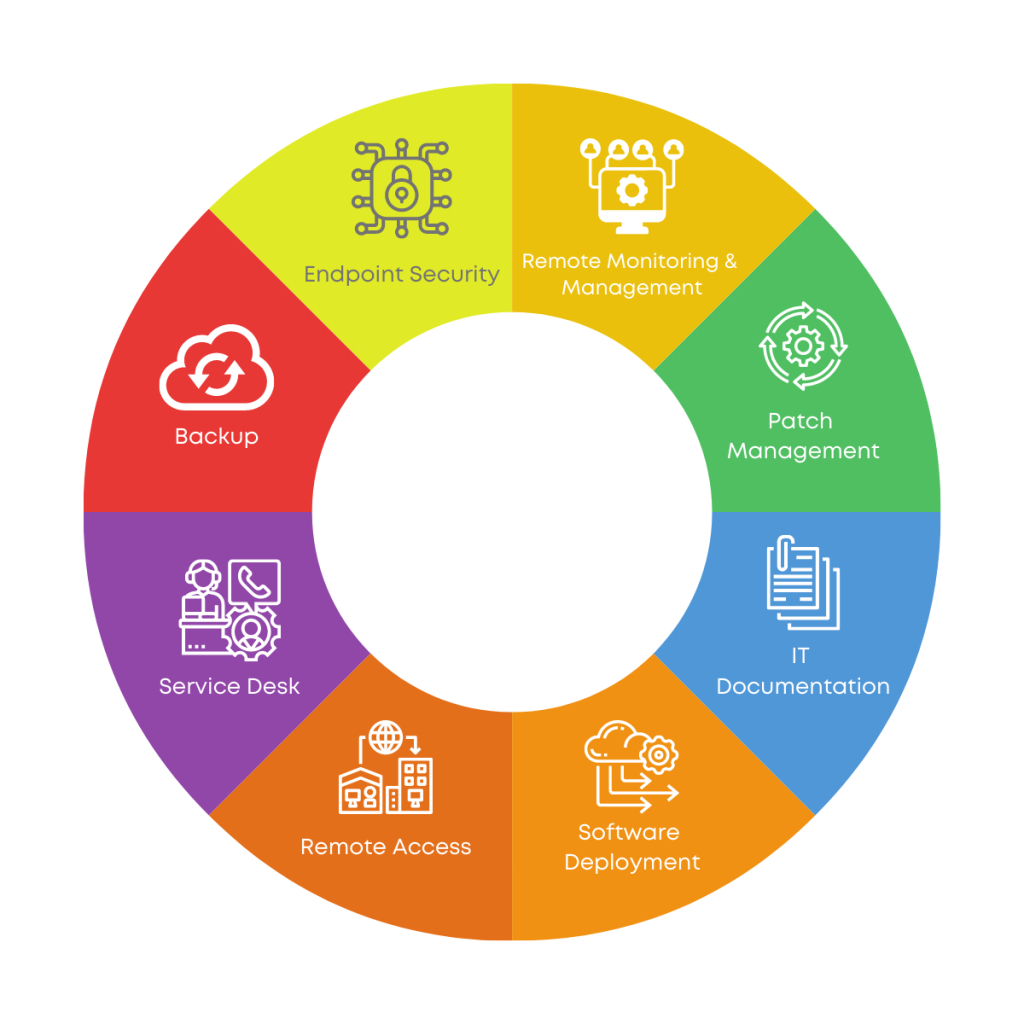
Key Components of RMM Solutions
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions are comprised of several key components that work together to provide comprehensive IT management capabilities. These components are designed to automate routine tasks, enhance security, and improve overall IT efficiency.
Remote Access
Remote access is a fundamental component of RMM solutions, allowing IT professionals to connect to and manage devices remotely. This capability eliminates the need for physical presence at each device, significantly streamlining troubleshooting and maintenance processes.
- Secure Connections: RMM solutions use secure protocols, such as Secure Shell (SSH) and Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), to establish encrypted connections, safeguarding sensitive data during remote access.
- Multi-Platform Support: Modern RMM tools support a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices, enabling centralized management across diverse IT environments.
- User Permissions: RMM platforms allow administrators to define granular access permissions for different users, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access specific devices or systems.
Monitoring
RMM solutions provide real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing IT teams to track the health and performance of devices and applications. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- System Performance: RMM tools monitor key system metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network bandwidth. These insights help identify performance bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
- Security Monitoring: RMM solutions continuously monitor for security threats, including malware, unauthorized access attempts, and suspicious activity. They often integrate with security information and event management (SIEM) systems to provide a comprehensive security posture.
- Alerting and Notifications: RMM platforms generate alerts and notifications when predefined thresholds are exceeded or critical events occur. This proactive approach allows IT teams to respond quickly to issues and prevent downtime.
Management
RMM solutions offer comprehensive management capabilities, enabling IT professionals to control and configure devices and applications remotely. These features streamline routine tasks and improve IT efficiency.
- Software Deployment: RMM tools facilitate the deployment of software updates, patches, and applications across multiple devices simultaneously. This centralized approach ensures consistent software versions and reduces the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Patch Management: RMM solutions automate the process of identifying and installing security patches, minimizing the time and effort required to keep systems up-to-date. This proactive approach helps mitigate security risks and improve overall system stability.
- Device Configuration: RMM platforms allow IT teams to configure and manage device settings, such as network settings, user accounts, and security policies. This centralized control ensures consistent configurations across the IT infrastructure.
Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure
RMM solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure, including Active Directory, cloud platforms, and other management tools. This integration streamlines workflows and eliminates the need for disparate systems.
- Active Directory Integration: RMM tools often integrate with Active Directory, allowing them to leverage existing user accounts and group policies for managing devices and permissions.
- Cloud Platform Integration: RMM solutions can integrate with cloud platforms such as Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to manage cloud-based infrastructure and applications.
- API Integration: Many RMM solutions offer Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), enabling them to integrate with other third-party tools and services, expanding their functionality and creating a unified IT management environment.
Types of RMM Solutions

RMM solutions come in various forms, each catering to different needs and budgets. Understanding the different types of RMM solutions is crucial for choosing the best option for your organization.
Categorization by Target Audience
RMM solutions are often tailored to specific audience segments, each with unique needs and priorities.
- Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs): SMB-focused RMM solutions are typically designed to be user-friendly and affordable, offering essential features like remote access, patch management, and basic security monitoring. They often come with simplified pricing structures and support options.
- Enterprises: Enterprise-grade RMM solutions are built for large, complex IT environments. They offer advanced features like automation, scripting, comprehensive reporting, and integration with other enterprise tools. These solutions often require higher upfront investment and have more complex pricing models.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises RMM Solutions
The deployment model of an RMM solution can significantly impact its features, costs, and manageability.
- Cloud-Based RMM Solutions: Cloud-based solutions are hosted on a third-party server, making them accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. They typically offer a subscription-based pricing model, simplifying budgeting and eliminating the need for local infrastructure. Cloud-based RMM solutions are often more scalable and easier to manage, as updates and maintenance are handled by the vendor. However, they might raise concerns about data security and privacy, especially for organizations with sensitive data.
- On-Premises RMM Solutions: On-premises solutions are installed and managed directly on the organization’s servers. They provide greater control over data security and privacy, as the data remains within the organization’s network. However, on-premises solutions require significant upfront investment in hardware and software, as well as ongoing maintenance and support. They also might be less scalable than cloud-based solutions, requiring manual updates and configuration.
Comparison of RMM Solutions
Various RMM solutions exist, each with its own set of features, pricing models, and target audience.
- Basic RMM Solutions: These solutions typically offer essential features like remote access, patch management, and basic security monitoring. They are often more affordable and suitable for SMBs with limited IT resources.
Examples include Atera, ConnectWise Manage, and Kaseya VSA.
- Advanced RMM Solutions: Advanced solutions provide a wider range of features, including automation, scripting, comprehensive reporting, and integration with other IT tools. They are often more expensive but cater to larger organizations with complex IT environments.
Examples include Datto RMM, SolarWinds N-central, and NinjaOne.
- Specialized RMM Solutions: These solutions are designed for specific industries or use cases, offering tailored features and functionalities. They might focus on security, compliance, or specific technologies.
Examples include security-focused solutions like CrowdStrike Falcon, compliance-focused solutions like LogicManager, and cloud-specific solutions like CloudCheckr.
Applications of RMM in Different Industries
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions have become indispensable tools for businesses across various industries. They provide a comprehensive approach to managing IT infrastructure, streamlining operations, and enhancing security. RMM solutions are particularly valuable in sectors like healthcare, finance, and education, where data security, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency are paramount.
RMM in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations face unique challenges in managing their IT infrastructure, including the need to comply with stringent regulations like HIPAA and the increasing reliance on electronic health records (EHRs). RMM solutions play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by:
- Ensuring HIPAA compliance: RMM solutions can help healthcare organizations meet HIPAA compliance requirements by providing automated patch management, data encryption, and access control features. This ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive patient data.
- Improving EHR security: EHR systems are critical to patient care, and RMM solutions can help secure these systems by monitoring for vulnerabilities, implementing strong passwords, and providing real-time threat detection. This helps prevent data breaches and ensures the integrity of patient records.
- Optimizing IT infrastructure: RMM solutions can automate routine IT tasks, such as software updates and system backups, freeing up healthcare IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. This improves operational efficiency and reduces the risk of downtime, which is critical in a time-sensitive environment like healthcare.
Example: A large hospital system implemented an RMM solution to manage its network of medical devices. The solution enabled the IT team to monitor the devices for vulnerabilities and proactively patch them, preventing potential security breaches. This ensured the smooth operation of critical medical equipment and protected sensitive patient data.
RMM in Finance
Financial institutions are heavily reliant on technology, and any disruption to their IT infrastructure can have significant consequences. RMM solutions help financial institutions manage their IT environments effectively by:
- Enhancing security: Financial institutions are prime targets for cyberattacks, and RMM solutions can help protect against these threats by providing real-time threat monitoring, endpoint security, and data loss prevention features. This helps prevent data breaches and ensure the confidentiality of sensitive financial information.
- Meeting regulatory compliance: The financial industry is subject to strict regulatory compliance requirements, such as PCI DSS and SOX. RMM solutions can help financial institutions meet these requirements by providing automated compliance reporting, vulnerability scanning, and access control features.
- Improving operational efficiency: RMM solutions can automate routine IT tasks, such as system backups and software updates, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. This improves operational efficiency and reduces the risk of downtime, which can be costly for financial institutions.
Example: A major bank implemented an RMM solution to manage its network of ATMs. The solution enabled the bank to monitor the ATMs for vulnerabilities and proactively patch them, preventing potential security breaches. This ensured the availability of ATMs and protected sensitive customer data.
RMM in Education
Educational institutions face increasing demands for technology-driven learning environments, and RMM solutions can help them manage their IT infrastructure effectively by:
- Supporting remote learning: RMM solutions can help educational institutions support remote learning by providing secure access to school resources, managing student devices, and monitoring network performance. This ensures a seamless and secure learning experience for students.
- Enhancing security: Educational institutions are vulnerable to cyberattacks, and RMM solutions can help protect against these threats by providing endpoint security, network monitoring, and data loss prevention features. This helps prevent data breaches and protects sensitive student information.
- Improving operational efficiency: RMM solutions can automate routine IT tasks, such as software updates and system backups, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. This improves operational efficiency and reduces the risk of downtime, which can disrupt the learning process.
Example: A large university implemented an RMM solution to manage its network of student laptops. The solution enabled the IT team to remotely install software updates, monitor device performance, and provide technical support to students. This ensured a smooth and secure learning experience for students and reduced the workload on the IT staff.
Security Considerations with RMM
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions provide significant benefits for IT professionals, enabling them to efficiently manage and secure devices remotely. However, like any technology that involves remote access, RMM solutions also introduce security risks that must be carefully considered and mitigated. This section will explore the potential security risks associated with RMM, how these solutions mitigate vulnerabilities, and best practices for securing RMM deployments.
Security Risks Associated with Remote Access
RMM solutions rely on remote access to manage and monitor devices. This access can be a potential entry point for malicious actors if not properly secured. Here are some key security risks:
- Unauthorized Access: If an RMM solution is not adequately secured, unauthorized individuals could gain access to sensitive data and systems. This could lead to data breaches, system compromises, and other security incidents.
- Malware Infection: Malicious actors could exploit vulnerabilities in the RMM software or its infrastructure to inject malware into managed devices. This could compromise the security of individual devices and the entire network.
- Data Exfiltration: An attacker with access to the RMM platform could potentially exfiltrate sensitive data from managed devices, such as customer information, financial records, or intellectual property.
- Denial-of-Service Attacks: Attackers could target the RMM platform with denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, disrupting the management and monitoring capabilities of the solution and potentially impacting critical business operations.
Mitigating Security Vulnerabilities
RMM solutions are designed with security in mind, incorporating features and mechanisms to mitigate vulnerabilities and protect managed devices and data. Here are some common security measures:
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): RMM platforms often require MFA, which adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of authentication before granting access. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC allows administrators to assign specific permissions to users based on their roles and responsibilities. This ensures that users only have access to the information and resources they need to perform their tasks, limiting potential security risks.
- Encryption: RMM solutions typically use encryption to protect data in transit and at rest. This ensures that data is unreadable to unauthorized individuals even if it is intercepted.
- Regular Security Updates: RMM vendors regularly release security updates to address vulnerabilities and improve the overall security posture of the solution. It’s crucial to install these updates promptly to stay protected.
- Security Monitoring and Logging: RMM platforms often include security monitoring and logging capabilities that track user activity, identify suspicious behavior, and generate alerts in case of security incidents. These features enable timely detection and response to potential threats.
Best Practices for Securing RMM Deployments
In addition to the security features built into RMM solutions, there are several best practices that organizations can implement to enhance the security of their RMM deployments:
- Use Strong Passwords and Passphrases: Encourage users to create strong passwords and passphrases that are difficult to guess. This is particularly important for administrative accounts that have access to sensitive information and settings.
- Limit Access to Sensitive Information: Only grant access to sensitive information to authorized personnel who require it for their job functions. This helps minimize the potential impact of a security breach.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Isolate the RMM platform from the rest of the network to limit the potential impact of a security breach. This can help prevent attackers from gaining access to other systems and data.
- Regularly Review and Update Security Policies: Security policies should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the threat landscape and organizational needs. This helps ensure that security measures are effective and up-to-date.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security controls are working as intended. This helps proactively address potential security risks before they can be exploited.
- Train Users on Security Best Practices: Educate users about security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attacks, using strong passwords, and reporting suspicious activity. This helps create a culture of security awareness within the organization.
Implementing an RMM Solution
Implementing a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solution is a crucial step in optimizing IT operations and enhancing security. The process involves careful selection, deployment, and ongoing configuration to ensure the solution aligns with your specific business needs.
Selecting an RMM Solution
Choosing the right RMM solution is essential for a successful implementation. Consider factors like your business size, budget, technical expertise, and specific requirements. Here’s a checklist to assess RMM vendors and their offerings:
- Features and Functionality: Evaluate the range of features offered, including remote access, patch management, endpoint security, and reporting capabilities. Ensure the solution aligns with your current and future IT needs.
- Scalability: Select a solution that can scale with your business growth. Consider the number of devices you need to manage and the potential for future expansion.
- Integration: Check if the RMM solution integrates with your existing IT infrastructure, such as Active Directory, ticketing systems, and security tools.
- Ease of Use: Choose a user-friendly interface that is intuitive for both IT professionals and end-users. Consider the learning curve and training requirements.
- Support and Documentation: Assess the vendor’s support options, including technical support, online resources, and community forums. Adequate documentation and training materials are crucial for successful implementation.
- Pricing: Compare pricing models, such as per-device, per-user, or subscription-based. Ensure the pricing aligns with your budget and the value offered.
Deploying an RMM Solution
Once you’ve selected an RMM solution, deploying it involves a series of steps:
- Installation: Install the RMM agent on all managed devices. This involves configuring the agent to connect to the RMM server.
- Configuration: Configure the RMM solution to meet your specific business needs. This includes setting up policies, alerts, and reports.
- Testing: Thoroughly test the RMM solution to ensure it is functioning correctly. Run simulated scenarios to validate its effectiveness.
- Training: Provide training to your IT staff on using the RMM solution. This includes understanding its features, functionalities, and troubleshooting techniques.
Customizing an RMM Solution
To maximize the value of your RMM solution, customize it to align with your unique requirements. This involves:
- Defining Policies: Establish clear policies for device management, software updates, and security configurations. Customize the RMM solution to enforce these policies.
- Setting Up Alerts: Configure alerts to notify you of critical events, such as system failures, security breaches, or unauthorized access. Customize the alert thresholds and notification methods to meet your needs.
- Creating Reports: Generate customized reports to track key metrics, such as device performance, software usage, and security vulnerabilities. Use these reports to identify trends, optimize resources, and make informed decisions.
Case Studies of Successful RMM Implementations
Real-world examples of companies that have successfully implemented RMM solutions offer valuable insights into the benefits and strategies involved. By examining these case studies, we can understand how RMM has helped businesses achieve improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced security.
Case Study: A Healthcare Provider
This healthcare provider faced challenges in managing a growing network of medical devices and workstations. They implemented an RMM solution to remotely monitor and manage their IT infrastructure. The solution allowed them to proactively identify and address issues before they impacted patient care.
- Benefits:
- Reduced downtime: The RMM solution enabled the IT team to identify and resolve issues before they escalated, minimizing disruptions to patient care.
- Improved security: The RMM solution provided real-time security monitoring and patch management, helping the healthcare provider to comply with HIPAA regulations and protect sensitive patient data.
- Enhanced efficiency: By automating tasks like software updates and patch management, the RMM solution freed up the IT team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Key Factors Contributing to Success:
- Clear objectives: The healthcare provider had a clear understanding of the challenges they faced and the goals they wanted to achieve with RMM.
- Proper planning and implementation: The healthcare provider carefully planned the implementation of the RMM solution, ensuring it was integrated with their existing IT infrastructure.
- Strong IT team: The healthcare provider had a dedicated IT team that was trained on the RMM solution and committed to its successful implementation.
Case Study: A Financial Services Company
A financial services company with multiple branches across the country needed a solution to manage their distributed IT infrastructure. They implemented an RMM solution to centralize their IT management and improve security.
- Benefits:
- Reduced costs: The RMM solution allowed the financial services company to reduce their IT support costs by automating tasks and providing remote access to their IT infrastructure.
- Improved security: The RMM solution provided real-time security monitoring and patch management, helping the financial services company to comply with industry regulations and protect sensitive customer data.
- Increased efficiency: The RMM solution enabled the IT team to manage their IT infrastructure from a central location, improving their efficiency and productivity.
- Key Factors Contributing to Success:
- Comprehensive solution: The financial services company selected an RMM solution that met their specific needs, including remote access, patch management, and security monitoring.
- Strong vendor support: The financial services company worked with a reputable RMM vendor that provided ongoing support and training.
- Integration with existing systems: The financial services company ensured that the RMM solution integrated seamlessly with their existing IT infrastructure.
Case Study: An Educational Institution
An educational institution with a large student body and a complex IT infrastructure needed a solution to manage their IT resources effectively. They implemented an RMM solution to provide remote support to students and staff and ensure the smooth operation of their IT systems.
- Benefits:
- Improved student experience: The RMM solution allowed the educational institution to provide students with quick and efficient IT support, enhancing their learning experience.
- Reduced IT costs: The RMM solution enabled the educational institution to reduce their IT support costs by automating tasks and providing remote access to their IT infrastructure.
- Enhanced security: The RMM solution provided real-time security monitoring and patch management, helping the educational institution to protect its IT infrastructure from cyber threats.
- Key Factors Contributing to Success:
- User-friendly interface: The educational institution selected an RMM solution with a user-friendly interface that was easy for students and staff to use.
- Scalability: The RMM solution was scalable to meet the growing needs of the educational institution.
- Strong vendor support: The educational institution worked with a reputable RMM vendor that provided ongoing support and training.
The Future of Remote Monitoring and Management
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) technology has been revolutionizing IT management for years, and its evolution shows no signs of slowing down. The future of RMM is brimming with exciting possibilities, driven by emerging trends like artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, as well as the ever-increasing complexity of IT environments.
Impact of AI and Automation on RMM
The integration of AI and automation is poised to transform RMM into a more proactive and intelligent system.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered RMM solutions can analyze historical data and identify patterns to predict potential issues before they occur. This allows IT teams to proactively address problems, minimizing downtime and improving system stability.
- Automated Remediation: RMM solutions can be automated to perform routine tasks like software updates, patch management, and security checks. This frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Security: AI-powered RMM solutions can detect and respond to security threats in real time. This includes identifying malicious activity, blocking suspicious connections, and implementing appropriate security measures.
RMM and the Rise of Remote Work
The rise of remote work has been a significant trend in recent years, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing work preferences, and the need for greater flexibility. This shift has created new challenges for businesses, particularly in managing and securing their IT infrastructure and devices, which are now scattered across diverse locations. Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions have emerged as critical tools for addressing these challenges, enabling organizations to effectively manage their remote workforces and ensure business continuity.
The Essential Role of RMM in Supporting Remote Workforces
RMM solutions have become indispensable for supporting remote workforces by providing centralized control and visibility over devices and systems, regardless of their physical location. They empower IT teams to manage, monitor, and secure devices remotely, ensuring seamless operations and productivity for employees working from home, co-working spaces, or other remote locations.
Managing and Securing Devices Remotely: Challenges and Solutions
Managing and securing devices remotely poses significant challenges, including:
- Device Configuration and Updates: Ensuring consistent configurations and timely updates across a dispersed workforce can be a complex task. RMM solutions streamline this process by enabling automated software deployment and patch management, ensuring all devices are running the latest versions of critical software and security updates.
- Security Threats and Vulnerability Management: Remote devices are more vulnerable to cyberattacks due to their dispersed nature. RMM solutions enhance security by providing real-time threat monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and endpoint security management. They can detect and respond to security threats proactively, minimizing the risk of data breaches and downtime.
- Data Loss Prevention: Data loss is a major concern for businesses with remote workforces. RMM solutions offer data loss prevention capabilities, such as data encryption, access control, and data backup and recovery, to safeguard sensitive information and ensure business continuity in the event of a device failure or security incident.
How RMM Solutions Help Organizations Effectively Manage Remote Employees
RMM solutions offer a comprehensive suite of tools and features that empower organizations to effectively manage their remote employees, including:
- Remote Device Management: RMM solutions allow IT teams to remotely manage and configure devices, including desktops, laptops, servers, and mobile devices. This enables them to troubleshoot issues, install software, and apply security updates without physically accessing the devices.
- Remote Monitoring and Performance Management: RMM solutions provide real-time monitoring of device performance, system health, and resource utilization. This allows IT teams to identify and address performance bottlenecks, proactively prevent issues, and ensure optimal system performance.
- Remote Support and Help Desk: RMM solutions integrate with help desk ticketing systems, allowing IT teams to provide remote support to employees experiencing technical difficulties. This streamlines the support process and reduces resolution time, ensuring employees can quickly get back to work.
- Security and Compliance: RMM solutions play a critical role in maintaining security and compliance for remote workforces. They offer features such as antivirus protection, firewall management, data encryption, and user access control to protect sensitive information and comply with industry regulations.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of RMM Solutions
Implementing a remote monitoring and management (RMM) solution can significantly impact an organization’s IT infrastructure and operations. However, the decision to adopt RMM requires a thorough cost-benefit analysis to understand the potential return on investment (ROI) and the associated costs.
This section will delve into the financial aspects of RMM, exploring the potential benefits and costs, and ultimately demonstrating how RMM can lead to long-term cost savings for organizations.
Quantifying the Return on Investment (ROI) of RMM
RMM solutions offer a multitude of benefits that can translate into tangible financial gains for organizations. The ROI of RMM can be quantified by considering the following key factors:
- Reduced IT Support Costs: RMM automates routine tasks, such as software updates, patch management, and system monitoring, freeing up IT staff to focus on more complex issues. This can lead to a significant reduction in labor costs. For example, a study by Spiceworks found that organizations using RMM reported an average reduction of 15% in their IT support costs.
- Improved System Uptime and Availability: RMM solutions proactively identify and resolve potential issues before they escalate into major outages, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. Increased uptime translates into improved productivity and revenue generation. A study by Gartner found that organizations using RMM experienced an average reduction of 20% in downtime.
- Enhanced Security Posture: RMM tools can help organizations identify and mitigate security threats, such as malware infections and unauthorized access attempts, reducing the risk of data breaches and costly security incidents. According to a report by Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 is $4.24 million.
- Increased IT Efficiency: RMM solutions streamline IT processes, allowing IT staff to manage multiple devices and systems from a central console. This improves efficiency and productivity, enabling IT teams to respond faster to incidents and manage their workload effectively.
Costs Associated with RMM Solutions
While RMM offers significant benefits, it’s important to consider the associated costs. These costs can be categorized as follows:
- Software Licensing: RMM solutions typically require a monthly or annual subscription fee based on the number of devices managed. The cost of software licensing can vary depending on the features and capabilities of the chosen RMM solution.
- Hardware: In some cases, RMM solutions may require additional hardware, such as a dedicated server or network appliances. However, cloud-based RMM solutions often eliminate the need for additional hardware.
- Training: IT staff may require training to effectively use and manage the RMM solution. Training costs can vary depending on the complexity of the RMM software and the number of staff being trained.
- Implementation: Implementing an RMM solution can require initial setup and configuration costs. This may involve hiring external consultants or allocating internal resources for the implementation process.
Demonstrating Long-Term Cost Savings
RMM solutions can lead to significant cost savings in the long run by reducing IT support costs, minimizing downtime, enhancing security, and improving IT efficiency.
To illustrate the potential cost savings, consider a hypothetical organization with 100 employees. Assume the organization currently spends $10,000 per month on IT support, experiences an average of 5 hours of downtime per month, and suffers a data breach every two years, costing $1 million. By implementing an RMM solution, the organization could potentially achieve the following:
- Reduced IT Support Costs: A 15% reduction in IT support costs would result in a monthly savings of $1,500.
- Reduced Downtime: A 20% reduction in downtime would result in a monthly savings of $2,000.
- Reduced Security Incidents: By mitigating security threats, the organization could potentially avoid a data breach, saving $1 million every two years.
Based on these estimates, the organization could save over $18,000 per year in IT support costs, downtime, and security incidents.
These savings can quickly outweigh the initial investment in RMM, making it a worthwhile investment for organizations looking to optimize their IT infrastructure and operations.
Best Practices for Effective RMM Utilization
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions are powerful tools for enhancing IT efficiency and security. However, to truly maximize their benefits, adopting a strategic approach to RMM implementation and utilization is crucial. This section Artikels best practices to ensure you’re getting the most out of your RMM investment.
Optimizing RMM Configuration
Proper configuration is essential for an effective RMM solution. It ensures the solution aligns with your specific needs and maximizes its potential. Here are some key areas to focus on:
- Define Clear Objectives: Before configuring your RMM solution, clearly define your objectives. Are you primarily focused on security, performance monitoring, or automating tasks? Having clear objectives will guide your configuration choices and ensure the solution meets your specific requirements.
- Establish Baselines and Thresholds: Define baselines and thresholds for key performance indicators (KPIs) like CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space. This allows the RMM solution to automatically trigger alerts when thresholds are breached, enabling proactive issue resolution.
- Configure Alerts and Notifications: Set up alerts and notifications for critical events and potential problems. Choose appropriate notification methods, such as email, SMS, or in-app notifications, based on your team’s preferences and the urgency of the situation.
- Implement Automated Patching: Configure automated patching schedules to ensure systems are always up-to-date with the latest security patches. This helps mitigate vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of security breaches.
- Customize Reporting: Leverage RMM reporting capabilities to generate customized reports on system health, security posture, and other relevant metrics. These reports provide valuable insights into your IT environment and can be used for decision-making and improvement initiatives.
Leveraging RMM for Proactive IT Management
RMM solutions go beyond reactive troubleshooting; they enable proactive IT management, which is crucial for maintaining system stability and preventing issues before they arise. Here’s how you can leverage RMM for proactive management:
- Regularly Monitor System Health: Utilize RMM dashboards and reports to regularly monitor system health and performance. Identify potential issues before they become critical, allowing for timely intervention and preventing disruptions.
- Implement Predictive Analytics: Some advanced RMM solutions offer predictive analytics capabilities. These features analyze historical data to identify patterns and predict potential problems, enabling you to take preventive measures before issues occur.
- Automate Routine Tasks: Automate repetitive tasks like software updates, system backups, and security scans. This frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives and improves operational efficiency.
- Proactive Security Measures: Use RMM to implement proactive security measures like vulnerability scanning, endpoint protection, and intrusion detection. This helps identify and mitigate security threats before they can exploit vulnerabilities.
- Optimize Resource Utilization: Analyze resource usage data from RMM reports to identify areas where optimization is possible. This can include identifying underutilized resources, optimizing system configurations, and implementing load balancing strategies.
Enhancing RMM Effectiveness
Beyond configuration and proactive management, there are additional practices that can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your RMM solution:
- Train Your Team: Ensure your IT team is well-trained on using the RMM solution effectively. This includes understanding its features, configuring alerts, and troubleshooting common issues. Proper training empowers your team to leverage the full potential of the RMM solution.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Continuously review your RMM configuration and settings. As your IT environment evolves, so should your RMM strategy. Regularly adjust settings, add new devices, and refine alerts based on changing needs.
- Integrate with Other Tools: Explore integration possibilities with other IT tools you use, such as ticketing systems, security information and event management (SIEM) platforms, and cloud services. This can create a more comprehensive and automated IT management ecosystem.
- Stay Updated with Latest Features: RMM solutions are constantly evolving with new features and capabilities. Stay informed about the latest updates and enhancements to ensure you’re leveraging the most advanced functionalities.
- Seek Expert Guidance: If you’re new to RMM or need help optimizing your implementation, consider seeking guidance from experienced IT professionals or consulting with RMM vendors. Their expertise can help you avoid common pitfalls and maximize the benefits of your RMM solution.
Ending Remarks
In today’s dynamic technological landscape, remote monitoring and management solutions are no longer a luxury but a necessity. By embracing RMM, organizations can gain a competitive edge by ensuring optimal IT performance, maximizing efficiency, and safeguarding sensitive data. As technology continues to evolve, RMM solutions will undoubtedly play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of IT management.
Remote monitoring and management tools can be incredibly helpful for managing and securing your devices, especially if you’re working with a large number of computers. For example, you might use these tools to install essential software like ms office free download for windows 10 across your network, ensuring all users have access to the latest productivity suite.
This type of remote management can significantly streamline your IT operations and enhance overall efficiency.