Remote management monitoring tool, a powerful suite of technologies, allows you to keep a watchful eye on your systems and devices from anywhere in the world. This capability empowers you to manage, troubleshoot, and optimize your infrastructure, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing downtime.
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where you can monitor your servers, network devices, and applications in real-time, regardless of your physical location. Remote management monitoring tools make this a reality, providing you with the tools to proactively identify and address potential issues before they impact your business.
What is a Remote Management and Monitoring Tool?
Remote management and monitoring tools are software applications that allow users to manage and monitor devices, networks, and applications remotely. These tools provide a centralized platform for managing and overseeing various aspects of IT infrastructure, offering insights into system performance, security, and overall health.
Purpose of Remote Management and Monitoring Tools
Remote management and monitoring tools serve a crucial purpose in today’s interconnected world, enabling organizations to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and ensure optimal performance of their IT infrastructure. They offer a comprehensive suite of capabilities that empower administrators to proactively manage and troubleshoot issues, regardless of their physical location.
Key Features of Remote Management and Monitoring Tools: Remote Management Monitoring Tool
Remote management and monitoring tools offer a wide range of features designed to streamline IT operations, enhance security, and improve overall system performance. These tools are essential for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to manage and monitor their IT infrastructure effectively, regardless of location.
Asset Management
Asset management is a crucial aspect of any IT infrastructure. It involves identifying, tracking, and managing all hardware and software assets within an organization. Remote management and monitoring tools provide comprehensive asset management capabilities, simplifying the process of keeping track of valuable IT resources.
- Automatic Discovery: These tools can automatically scan the network to identify all connected devices, including servers, workstations, routers, and switches. This helps create a comprehensive inventory of assets, ensuring nothing is missed.
- Hardware and Software Inventory: Remote management tools provide detailed information about each asset, including hardware specifications, software versions, operating systems, and license details. This information is essential for planning upgrades, managing software licenses, and ensuring compliance.
- Asset Tracking and Reporting: These tools allow you to track asset movements, monitor usage patterns, and generate reports on asset utilization. This data helps optimize resource allocation, identify underutilized assets, and make informed decisions about future investments.
Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring is essential for ensuring optimal system performance and identifying potential issues before they impact users. Remote management and monitoring tools provide real-time insights into system performance, allowing IT teams to proactively address any performance bottlenecks or degradation.
- System Metrics Monitoring: These tools monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, network bandwidth, and application response times. Real-time monitoring helps identify performance issues early and prevent them from escalating.
- Alerting and Notifications: When performance metrics exceed predefined thresholds, the tools trigger alerts and notifications, informing IT teams about potential problems. This allows for prompt intervention and prevents downtime.
- Performance Analysis and Reporting: Remote management tools generate comprehensive performance reports, providing historical data and trend analysis. This information helps identify performance patterns, optimize resource allocation, and make data-driven decisions about system upgrades or capacity planning.
Security
Security is paramount in today’s digital landscape. Remote management and monitoring tools play a crucial role in securing IT infrastructure by providing real-time threat detection, vulnerability assessment, and security incident response capabilities.
- Security Event Logging: These tools capture and log security events, such as failed login attempts, unauthorized access attempts, and malware detection. This information helps identify security threats and track potential vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Remote management tools can perform regular vulnerability scans to identify security weaknesses in the network and individual devices. This allows for proactive patching and mitigation of potential security risks.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Some tools incorporate intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and block malicious attempts to access the network. This helps protect against various cyberattacks and data breaches.
Reporting
Comprehensive reporting is essential for gaining insights into IT infrastructure performance, security posture, and overall health. Remote management and monitoring tools generate detailed reports that provide valuable information for decision-making, troubleshooting, and optimization.
- Customizable Reports: These tools offer customizable reporting options, allowing IT teams to generate reports tailored to their specific needs and requirements. This enables them to focus on critical metrics and gain actionable insights.
- Trend Analysis: Remote management tools can analyze historical data to identify trends and patterns in system performance, security events, and asset utilization. This information helps predict future issues, plan capacity upgrades, and optimize resource allocation.
- Compliance Reporting: Some tools generate reports that meet specific compliance requirements, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. This helps organizations demonstrate compliance and ensure their IT infrastructure meets regulatory standards.
Implementing Remote Management and Monitoring Tools
Implementing a remote management and monitoring tool requires a structured approach to ensure successful integration within an organization’s IT infrastructure. This process involves careful planning, selection, deployment, and ongoing management.
Challenges During Implementation
The implementation of remote management and monitoring tools can present various challenges, which can be mitigated with strategic planning and execution. These challenges often arise from factors like:
- Compatibility Issues: Integrating the tool with existing systems and applications can pose compatibility challenges, requiring thorough testing and potential modifications to ensure seamless operation.
- Security Concerns: Remote access to critical systems raises security concerns, necessitating robust security measures like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and access control policies to prevent unauthorized access.
- Training and Adoption: Proper training for users and IT staff is essential to ensure effective utilization of the tool’s features and functionalities. Lack of training can lead to resistance and reduced adoption rates.
- Data Management and Storage: The tool generates large amounts of data, requiring efficient storage and management solutions to avoid performance issues and ensure data integrity.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
Overcoming these challenges requires a proactive approach:
- Thorough Planning and Testing: Conduct thorough planning and testing to ensure compatibility with existing systems and applications. This includes compatibility testing with different operating systems, network configurations, and existing software.
- Robust Security Measures: Implement robust security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and access control policies, to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are also crucial.
- Comprehensive Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training programs for users and IT staff to familiarize them with the tool’s features, functionalities, and best practices. Ongoing support through documentation, FAQs, and dedicated support teams is also essential.
- Data Management Solutions: Implement efficient data management solutions, such as data compression, data deduplication, and cloud storage, to manage the large volumes of data generated by the tool. This ensures data integrity and prevents performance issues.
Process of Selecting, Deploying, and Integrating a Remote Management and Monitoring Tool
The process of selecting, deploying, and integrating a remote management and monitoring tool can be represented by a flowchart:
Flowchart:
Step 1: Define Requirements: Identify the specific needs and requirements for remote management and monitoring.
Step 2: Research and Evaluate Tools: Research available tools, evaluate their features, functionalities, and pricing, and compare them based on your requirements.
Step 3: Select a Tool: Choose the tool that best meets your needs and budget.
Step 4: Plan Deployment: Develop a deployment plan, including infrastructure requirements, security measures, and user training.
Step 5: Install and Configure the Tool: Install and configure the tool according to the deployment plan.
Step 6: Integrate with Existing Systems: Integrate the tool with existing systems and applications.
Step 7: Test and Optimize: Conduct thorough testing to ensure the tool is working as expected and optimize its performance.
Step 8: Implement Monitoring and Reporting: Configure monitoring and reporting to track performance, identify issues, and generate insights.
Step 9: Ongoing Management and Support: Provide ongoing management and support, including updates, security patches, and user assistance.
Best Practices for Effective Remote Management and Monitoring
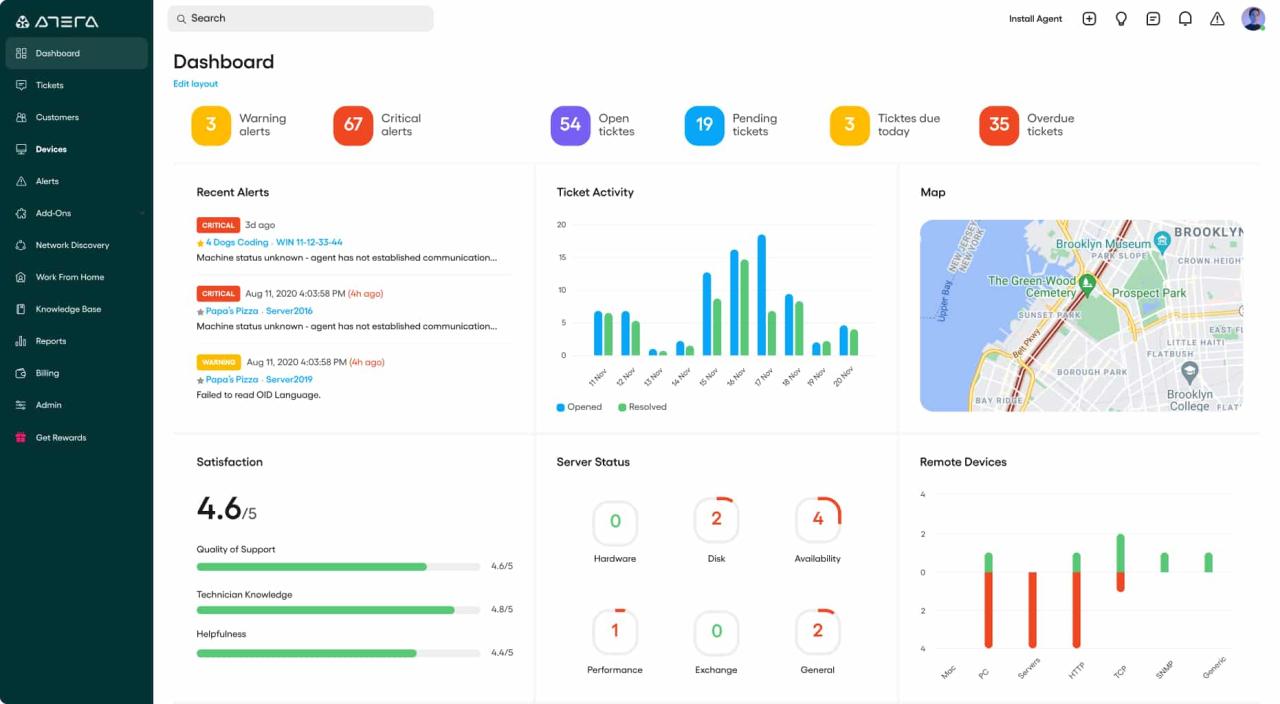
Remote management and monitoring tools offer a powerful way to streamline IT operations, improve system performance, and enhance security. However, maximizing their benefits requires implementing best practices that ensure effective utilization and insightful data analysis.
Setting Up Alerts
Effective alert configuration is crucial for timely problem identification and swift resolution.
- Define clear alert thresholds: Establish specific values for metrics that trigger alerts. For instance, set CPU utilization thresholds for servers, network bandwidth limits, or disk space warnings. This ensures that alerts are triggered only when significant deviations occur, preventing alert fatigue.
- Prioritize alert severity: Classify alerts based on their impact, using severity levels like critical, major, minor, or informational. This helps prioritize responses, focusing on critical issues first. For example, a critical alert might be triggered for a server outage, while a minor alert could indicate a temporary network hiccup.
- Configure alert routing: Determine the appropriate recipients for each alert based on their role and expertise. For example, network administrators might receive alerts related to network performance, while security analysts could be notified of potential security breaches. This ensures that alerts reach the right people for prompt action.
- Implement escalation procedures: Establish a clear escalation process for alerts that remain unresolved after a certain time. This ensures that issues are escalated to higher-level personnel when necessary, facilitating timely resolution. For instance, if a critical alert for a server outage remains unaddressed for an extended period, it should be escalated to a senior system administrator.
Configuring Dashboards
Well-designed dashboards provide a centralized view of system health, performance, and security.
- Choose relevant metrics: Select metrics that provide meaningful insights into system performance, security, and resource utilization. For example, dashboards for servers might include CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network traffic. Security dashboards could track intrusion attempts, malware detections, and firewall activity.
- Visualize data effectively: Utilize charts, graphs, and other visualizations to present data clearly and concisely. This enhances understanding and facilitates quick identification of trends and anomalies. For example, line graphs can depict CPU usage over time, while heatmaps can highlight areas of high network traffic.
- Group related metrics: Organize dashboards to group related metrics together, enhancing usability and clarity. For example, a server dashboard might include sections for CPU, memory, disk space, and network traffic, while a security dashboard could group metrics related to intrusion detection, malware analysis, and firewall activity.
- Customize dashboards for different roles: Create separate dashboards tailored to the needs of specific roles within the organization. For instance, network administrators might require detailed network performance dashboards, while security analysts may need dashboards focused on security threats and vulnerabilities.
Analyzing Data
Effective data analysis is key to gaining actionable insights from remote monitoring data.
- Identify trends and patterns: Analyze historical data to identify recurring patterns and trends in system performance, security events, and resource usage. This helps predict future issues and proactively address potential problems. For example, analyzing historical network traffic data can reveal peak usage times, allowing for capacity planning and network optimization.
- Correlate data from multiple sources: Analyze data from different sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of system behavior. For instance, correlating server performance data with network traffic data can identify bottlenecks and network issues impacting server performance.
- Use automated reporting: Leverage automated reporting features to generate regular reports on system performance, security events, and resource usage. This provides a structured overview of system health and helps identify areas requiring attention. For example, weekly reports on server performance and security incidents can highlight potential issues and guide proactive maintenance efforts.
- Implement data visualization tools: Utilize data visualization tools to create interactive dashboards and reports that allow for deeper analysis and exploration of data. This enables users to drill down into specific areas of interest and gain a more granular understanding of system behavior.
Real-World Examples
- Proactive server maintenance: By analyzing historical server performance data, an IT team identified a recurring pattern of high CPU utilization during peak business hours. Based on this insight, they proactively upgraded server hardware, preventing performance issues and ensuring smooth operations during peak periods.
- Security incident detection: A remote monitoring tool detected a suspicious increase in login attempts from an unusual geographic location. This triggered an alert, prompting security analysts to investigate further. They discovered a brute-force attack targeting user accounts, enabling them to take immediate action to mitigate the threat.
- Network optimization: By analyzing network traffic data, a company identified a bottleneck in their network infrastructure. They used this information to optimize network routing and upgrade network hardware, improving overall network performance and reducing latency.
Security Considerations for Remote Management and Monitoring Tools
Remote management and monitoring tools, while offering significant benefits in terms of efficiency and accessibility, also introduce a range of security risks that must be carefully addressed. These tools often require access to sensitive data and systems, making them prime targets for malicious actors. Therefore, implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect both the tools themselves and the data they manage.
Security Risks Associated with Remote Management and Monitoring Tools
Remote management and monitoring tools inherently involve connecting to systems and networks remotely, making them susceptible to various security risks. These risks can be categorized as follows:
- Unauthorized Access: Unsecured connections or weak authentication mechanisms can allow unauthorized individuals to gain access to the tool, compromising sensitive data and systems. For example, an attacker could exploit a vulnerability in the tool’s software to gain access and steal data, or they could intercept network traffic to obtain credentials.
- Data Breaches: The data collected and managed by these tools can be highly sensitive, including confidential information about users, systems, and network activity. A breach of this data could lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. For instance, a hacker could steal customer data from a remote monitoring tool, leading to identity theft and fraud.
- Denial of Service Attacks: Attackers can target remote management and monitoring tools with denial-of-service attacks, disrupting the tool’s functionality and hindering the ability to manage and monitor systems effectively. This could impact critical operations and cause significant downtime.
- Malware Infection: Remote management and monitoring tools can become infected with malware, allowing attackers to gain control of the tool and use it to spread malware to other systems or steal data. For example, an attacker could inject malicious code into the tool’s software, which could then be used to compromise connected systems.
- Misconfiguration: Improperly configured remote management and monitoring tools can create security vulnerabilities. For instance, a misconfigured tool might allow access to sensitive data to unauthorized users or expose the tool to network attacks.
Best Practices for Securing Remote Management and Monitoring Tools, Remote management monitoring tool
Implementing robust security practices is essential to mitigate the risks associated with remote management and monitoring tools. These practices include:
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, making it more difficult for attackers to gain access.
- Secure Communication: Ensure that all communication between the tool and managed systems is encrypted using protocols like HTTPS or SSH. This protects data from interception and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Regular Security Updates: Keep the tool’s software up to date with the latest security patches and updates. This addresses vulnerabilities and mitigates potential risks. Regular updates ensure that the tool is protected against known security flaws.
- Access Control: Implement granular access control policies to restrict access to specific functionalities and data based on user roles and permissions. This ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information and systems.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate the remote management and monitoring tool from other sensitive systems and networks. This reduces the potential impact of a security breach on other critical systems.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. This includes penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security assessments to identify potential weaknesses in the tool’s security posture.
- Security Awareness Training: Train users on best practices for securing remote management and monitoring tools and protecting sensitive data. This includes raising awareness of common threats, identifying phishing attacks, and understanding the importance of strong passwords.
Common Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Measures
Remote management and monitoring tools can be susceptible to various security vulnerabilities, including:
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): This vulnerability allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into the tool’s web interface, potentially stealing user credentials or compromising the tool’s functionality. Mitigation measures include input validation and output encoding to prevent the execution of malicious scripts.
- SQL Injection: This vulnerability allows attackers to manipulate database queries, potentially gaining access to sensitive data or manipulating data within the tool’s database. Mitigation measures include parameterized queries and input validation to prevent the injection of malicious code into database queries.
- Remote Code Execution (RCE): This vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the tool’s server, potentially gaining full control of the tool and the systems it manages. Mitigation measures include regularly patching vulnerabilities, implementing strong access control policies, and using secure coding practices.
Future Trends in Remote Management and Monitoring
The field of remote management and monitoring is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business needs. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud computing is reshaping the landscape, leading to more sophisticated and proactive solutions. These trends are poised to revolutionize how businesses manage and monitor their IT infrastructure, offering enhanced efficiency, security, and insights.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming remote management and monitoring by automating tasks, identifying anomalies, and providing predictive insights.
- Automated Incident Response: AI-powered systems can analyze data from various sources, detect potential issues, and automatically initiate corrective actions. This reduces human intervention and speeds up response times, minimizing downtime and improving service availability.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, ML algorithms can predict potential hardware failures before they occur. This allows organizations to schedule maintenance proactively, reducing the risk of unexpected outages and minimizing repair costs.
- Enhanced Security: AI and ML can be used to detect and prevent cyberattacks. They can analyze network traffic, identify suspicious activities, and automatically implement security measures, strengthening overall cybersecurity posture.
The Role of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is playing a significant role in enabling remote management and monitoring solutions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based platforms offer scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust their resources based on demand. This flexibility is crucial for organizations with fluctuating workloads or rapid growth.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud computing can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises solutions, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. This is because cloud providers handle infrastructure maintenance and upgrades, reducing operational costs.
- Improved Accessibility: Cloud-based solutions provide anytime, anywhere access to monitoring data, allowing IT teams to manage and monitor systems from any location with an internet connection.
Emerging Trends in Remote Management and Monitoring
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices is creating a massive amount of data that needs to be managed and monitored effectively. Remote management and monitoring solutions are becoming increasingly important for managing and securing IoT devices.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings data processing and analysis closer to the source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This trend is creating new opportunities for remote management and monitoring solutions that can operate in real-time at the edge.
- DevOps Integration: Remote management and monitoring tools are increasingly being integrated with DevOps practices, enabling organizations to monitor their applications and infrastructure throughout the entire development lifecycle.
Case Studies of Successful Remote Management and Monitoring Implementations
Remote management and monitoring tools have become essential for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to manage and monitor their IT infrastructure remotely. Many organizations have successfully implemented these tools, achieving significant benefits in terms of efficiency, cost savings, and improved security. This section explores case studies of organizations that have successfully implemented remote management and monitoring tools, highlighting the challenges they faced, the strategies they adopted, and the positive outcomes they achieved.
Case Study: XYZ Corporation
XYZ Corporation, a global technology company with offices in multiple countries, faced the challenge of managing a vast and complex IT infrastructure. They needed a solution to monitor their systems in real-time, detect potential issues before they became critical, and respond quickly to incidents.
XYZ Corporation decided to implement a remote management and monitoring tool that provided comprehensive visibility into their entire IT infrastructure. The tool allowed them to:
– Monitor critical systems: They could track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic.
– Proactively identify issues: The tool detected anomalies and alerted administrators to potential problems before they caused outages.
– Automate tasks: They automated routine tasks such as software updates and security patches, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
– Improve security: The tool helped them identify and mitigate security threats, reducing the risk of data breaches.
XYZ Corporation experienced significant benefits from implementing the remote management and monitoring tool. They reduced downtime, improved IT efficiency, and enhanced security.
Case Study: ABC Healthcare
ABC Healthcare, a large hospital system, faced the challenge of managing a geographically dispersed network of facilities. They needed a solution to monitor their medical devices, ensure patient safety, and comply with regulatory requirements.
ABC Healthcare implemented a remote management and monitoring tool specifically designed for healthcare organizations. The tool allowed them to:
– Monitor medical devices: They could track the status of critical medical equipment, such as ventilators and infusion pumps, in real-time.
– Ensure patient safety: The tool alerted administrators to potential issues with medical devices, preventing patient harm.
– Comply with regulations: The tool helped them meet regulatory requirements for data security and patient privacy.
ABC Healthcare saw a significant improvement in patient safety and regulatory compliance after implementing the remote management and monitoring tool. They also achieved cost savings by reducing the need for on-site technicians.
Case Study: DEF Manufacturing
DEF Manufacturing, a global manufacturing company, faced the challenge of managing a large and complex network of manufacturing facilities. They needed a solution to monitor their production lines, ensure efficient operations, and optimize their manufacturing processes.
DEF Manufacturing implemented a remote management and monitoring tool that provided real-time insights into their manufacturing processes. The tool allowed them to:
– Monitor production lines: They could track production output, identify bottlenecks, and optimize production efficiency.
– Reduce downtime: The tool detected potential issues with machines and equipment, allowing them to address problems before they caused downtime.
– Improve quality control: The tool helped them monitor product quality and identify areas for improvement.
DEF Manufacturing experienced a significant increase in production efficiency and a reduction in downtime after implementing the remote management and monitoring tool. They also improved their product quality and reduced manufacturing costs.
Key Takeaways
| Case Study | Challenges | Strategies | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| XYZ Corporation | Managing a vast and complex IT infrastructure | Implementing a comprehensive remote management and monitoring tool | Reduced downtime, improved IT efficiency, enhanced security |
| ABC Healthcare | Managing a geographically dispersed network of facilities, ensuring patient safety, complying with regulations | Implementing a healthcare-specific remote management and monitoring tool | Improved patient safety, enhanced regulatory compliance, reduced costs |
| DEF Manufacturing | Managing a large and complex network of manufacturing facilities, optimizing production processes | Implementing a remote management and monitoring tool for manufacturing | Increased production efficiency, reduced downtime, improved product quality, reduced costs |
Comparison of Popular Remote Management and Monitoring Tools

The market offers a wide array of remote management and monitoring tools, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. This section will compare some of the leading tools, analyzing their features, pricing, ease of use, and customer support. Understanding these differences can help you choose the best tool for your specific needs and budget.
Key Features and Comparisons
This section provides a comparative analysis of popular remote management and monitoring tools based on their key features. This comparison will help you understand the strengths and weaknesses of each tool, allowing you to make an informed decision based on your specific requirements.
| Tool | Features | Pricing | Ease of Use | Customer Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SolarWinds RMM | Patch management, endpoint security, remote control, asset management, reporting | Starts at $69.95 per month for up to 10 endpoints | User-friendly interface with intuitive navigation | Excellent customer support with 24/7 phone, email, and chat options |
| Datadog | Monitoring of infrastructure, applications, and logs, real-time dashboards, alerts, and integrations | Starts at $15 per month for up to 5 hosts | Modern and intuitive user interface, but requires some technical expertise | Excellent documentation and active community support |
| ManageEngine | Remote control, patch management, asset management, software distribution, reporting | Starts at $495 per year for up to 25 endpoints | User-friendly interface with comprehensive features | Good customer support with email and phone options |
| Atera | Remote control, patch management, ticketing system, billing and invoicing, reporting | Starts at $79 per month for up to 50 endpoints | Intuitive interface with a focus on automation and efficiency | Excellent customer support with 24/7 phone, email, and chat options |
| ConnectWise Manage | Ticketing system, service desk, project management, reporting, and integrations | Starts at $49 per month for up to 5 users | Comprehensive platform with a focus on service desk and project management | Excellent customer support with 24/7 phone, email, and chat options |
Remote Management and Monitoring Tools: A Comprehensive Guide
Remote management and monitoring tools are essential for businesses of all sizes, enabling efficient and effective management of IT infrastructure and applications. These tools provide real-time insights into system performance, security, and user behavior, allowing administrators to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact business operations. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of remote management and monitoring tools, from their key features and implementation strategies to best practices, security considerations, and future trends.
Benefits of Remote Management and Monitoring Tools
Remote management and monitoring tools offer numerous benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved System Performance: Real-time monitoring allows for early detection and resolution of performance bottlenecks, ensuring optimal system performance.
- Enhanced Security: These tools provide security alerts, intrusion detection, and vulnerability scanning, helping to protect against cyber threats.
- Reduced Downtime: Proactive monitoring and automated issue resolution minimize downtime, ensuring business continuity.
- Cost Savings: By automating tasks and reducing the need for on-site support, these tools can significantly lower operational costs.
- Increased Efficiency: Remote management capabilities enable administrators to manage multiple systems and applications from a single location, increasing efficiency and productivity.
- Improved Collaboration: Remote management tools facilitate collaboration among IT teams, enabling efficient problem-solving and knowledge sharing.
Types of Remote Management and Monitoring Tools
There are various types of remote management and monitoring tools available, each catering to specific needs:
- Network Management Tools: These tools monitor network performance, traffic, and security, providing insights into network health and potential issues.
- Server Management Tools: These tools allow for remote administration of servers, including performance monitoring, resource allocation, and security management.
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM) Tools: These tools monitor the performance of applications, identifying bottlenecks and performance issues that affect user experience.
- System Monitoring Tools: These tools provide comprehensive system monitoring, encompassing hardware, software, and network components, offering a holistic view of system health.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools: These tools aggregate security data from various sources, providing real-time threat detection and incident response capabilities.
Concluding Remarks
As we’ve explored, remote management monitoring tools offer a wealth of benefits, enabling businesses to streamline operations, enhance security, and achieve optimal performance. Whether you’re managing a small business or a large enterprise, embracing these tools is a strategic decision that can significantly impact your success.
Remote management monitoring tools are essential for businesses of all sizes, offering real-time insights into system performance and potential issues. One crucial aspect of managing data effectively is efficient compression, which is where tools like win zip come in.
By reducing file sizes, you can optimize storage space and speed up data transfer, further enhancing the efficiency of your remote management monitoring tool.
