Remote IT monitoring software is a powerful tool that empowers businesses to proactively manage their IT infrastructure, ensuring seamless operations and minimizing downtime. By providing real-time visibility into network, server, application, and security performance, this software empowers IT teams to identify potential issues before they escalate, enabling swift resolution and preventing disruptions to critical business processes.
Table of Contents
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of remote IT monitoring software, exploring its benefits, key features, different types, implementation considerations, and the latest trends shaping the industry. We will also examine how this technology can be seamlessly integrated with other tools to streamline workflows and enhance overall IT efficiency.
What is Remote IT Monitoring Software?
Remote IT monitoring software is a powerful tool that allows businesses to keep a watchful eye on their IT infrastructure, regardless of location. This software provides real-time insights into the performance, health, and security of devices, networks, and applications, enabling proactive maintenance and problem resolution.
Key Features and Functionalities
Remote IT monitoring software offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline IT operations and ensure optimal system performance. Some key functionalities include:
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks key metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network bandwidth to identify potential bottlenecks and performance issues.
- Availability Monitoring: Ensures critical systems and applications are up and running, alerting administrators to any downtime or service disruptions.
- Security Monitoring: Detects suspicious activities, security threats, and vulnerabilities, providing early warnings and enabling swift response to potential breaches.
- Log Management: Collects and analyzes system logs to identify patterns, diagnose issues, and track security events.
- Alerting and Notifications: Sends real-time alerts and notifications to designated personnel when predefined thresholds are breached or specific events occur.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generates detailed reports and dashboards to provide insights into system performance, security posture, and overall IT health.
Common Use Cases in Various Industries
Remote IT monitoring software finds widespread applications across various industries, enabling businesses to optimize their IT infrastructure and enhance operational efficiency. Some common use cases include:
- Healthcare: Monitoring medical equipment, patient databases, and critical systems to ensure uninterrupted service and patient safety.
- Financial Services: Ensuring the availability and security of financial transactions, customer data, and trading platforms.
- Manufacturing: Monitoring production lines, industrial control systems, and supply chain management to optimize efficiency and minimize downtime.
- Education: Ensuring the availability of learning management systems, online resources, and student data, enabling uninterrupted access to education.
- Retail: Monitoring POS systems, inventory management systems, and customer databases to enhance operational efficiency and customer experience.
Key Features of Remote IT Monitoring Software
Remote IT monitoring software is a powerful tool that provides businesses with comprehensive visibility into their IT infrastructure. This visibility enables proactive identification and resolution of issues before they impact operations, ensuring smooth business continuity. By leveraging the key features of remote IT monitoring software, businesses can enhance their IT infrastructure’s performance, security, and reliability.
Network Monitoring
Network monitoring is crucial for ensuring smooth data flow and optimal network performance. It involves tracking key network metrics such as bandwidth usage, latency, packet loss, and device connectivity.
- Real-time Network Performance Visualization: Network monitoring software provides real-time visualizations of network traffic patterns, identifying bottlenecks and potential issues. This allows for quick identification and resolution of network problems before they impact user experience.
- Network Topology Mapping: This feature provides a graphical representation of the network infrastructure, including devices, connections, and traffic flow. It aids in understanding the network’s structure and helps identify potential vulnerabilities or performance issues.
- Network Security Monitoring: Network monitoring tools can detect suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or malware infections. They can also monitor for vulnerabilities and alert administrators to potential security threats.
Server Monitoring
Server monitoring is essential for ensuring the stability and performance of critical applications and services. It involves tracking server resources, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network activity.
- Resource Utilization Monitoring: Server monitoring software tracks resource usage, identifying potential bottlenecks and capacity issues. This allows for proactive resource allocation and optimization, preventing performance degradation.
- Server Health and Availability Monitoring: It monitors server health parameters, such as temperature, fan speed, and power supply, alerting administrators to potential hardware failures. This proactive approach ensures server uptime and reduces downtime risks.
- Performance Optimization: By identifying resource-intensive processes and applications, server monitoring software helps optimize server performance. It allows administrators to prioritize resources and ensure optimal performance for critical applications.
Application Monitoring
Application monitoring focuses on tracking the performance and availability of critical business applications. It monitors metrics such as response times, error rates, and user activity, providing insights into application health and user experience.
- Performance Monitoring: Application monitoring software tracks application performance metrics, such as response times, throughput, and error rates. This allows for quick identification and resolution of performance issues, ensuring optimal user experience.
- Availability Monitoring: It ensures application uptime and availability by monitoring application status and detecting outages or performance degradations. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures business continuity.
- User Experience Monitoring: Application monitoring software can track user activity and identify potential bottlenecks or issues impacting user experience. This data helps optimize application performance and improve user satisfaction.
Security Monitoring
Security monitoring is crucial for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access. It involves monitoring network traffic, user activity, and system logs for suspicious patterns or security threats.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Security monitoring software can detect and prevent intrusions by analyzing network traffic and identifying suspicious activity. This helps protect against malware, unauthorized access, and other security threats.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Security monitoring tools can scan systems for vulnerabilities and identify potential security risks. This allows for proactive patching and remediation, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks.
- Security Incident Response: In the event of a security breach, security monitoring software can help track the incident, identify the source of the attack, and provide evidence for incident response and remediation efforts.
Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring is essential for identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks and optimizing system efficiency. It involves tracking system resources, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network activity.
- Resource Utilization Monitoring: Performance monitoring software tracks resource usage across the IT infrastructure, identifying potential bottlenecks and capacity issues. This allows for proactive resource allocation and optimization, preventing performance degradation.
- Performance Trend Analysis: It analyzes performance data over time, identifying trends and patterns that may indicate potential issues or areas for improvement. This proactive approach helps optimize system performance and prevent future problems.
- Performance Benchmarking: Performance monitoring software can compare system performance against industry benchmarks or historical data, identifying areas for improvement and optimizing system efficiency.
Alerting and Reporting
Alerting and reporting are critical for informing administrators of potential issues and providing insights into system performance and security. Remote IT monitoring software provides real-time alerts and comprehensive reports to ensure proactive problem resolution and informed decision-making.
- Real-time Alerts: Alerting systems notify administrators of critical events or potential issues, allowing for prompt intervention and minimizing downtime. These alerts can be customized to specific thresholds and triggers, ensuring relevant and timely notifications.
- Customizable Reporting: Remote IT monitoring software offers customizable reporting capabilities, allowing administrators to generate reports on various metrics, such as system performance, security events, and resource utilization. These reports provide valuable insights for informed decision-making and performance optimization.
- Trend Analysis and Forecasting: Reporting tools can analyze historical data and identify trends and patterns, providing insights into future performance and potential issues. This proactive approach allows for preventive measures and optimized resource allocation.
Types of Remote IT Monitoring Software
Remote IT monitoring software comes in various forms, catering to different needs and budgets. Understanding the different types can help you choose the right solution for your organization.
Deployment Model
The deployment model determines how the software is hosted and accessed.
- Cloud-based: Cloud-based solutions are hosted on a third-party server, making them accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure, simplifying setup and maintenance. Popular examples include Datadog, SolarWinds, and New Relic.
- On-premises: On-premises solutions are installed and managed directly on your organization’s servers. This provides greater control over data security and customization but requires dedicated IT resources for installation, maintenance, and updates. Examples include Nagios, Zabbix, and PRTG Network Monitor.
Target Audience
Remote IT monitoring software is designed for various audience sizes, with features tailored to specific needs.
- Small Businesses: Solutions for small businesses are typically user-friendly and affordable, focusing on basic monitoring features like server uptime, network performance, and basic security alerts. Examples include ManageEngine OpManager, Atera, and Kaseya.
- Enterprises: Enterprise-grade solutions offer advanced features like real-time performance dashboards, automated incident response, and integration with other IT tools. They are designed to manage complex IT infrastructures and large data volumes. Examples include Splunk, Dynatrace, and AppDynamics.
Monitoring Capabilities
The level of monitoring capabilities determines the depth and breadth of insights provided by the software.
- Basic: Basic monitoring solutions focus on essential metrics like server uptime, network connectivity, and basic performance indicators. They provide alerts for critical issues but lack in-depth analysis and predictive capabilities. Examples include Pingdom, UptimeRobot, and StatusCake.
- Advanced: Advanced monitoring solutions offer comprehensive insights into system performance, resource utilization, and user experience. They provide real-time dashboards, performance analysis, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Examples include Datadog, SolarWinds, and New Relic.
Choosing the Right Remote IT Monitoring Software

The process of selecting the right remote IT monitoring software involves carefully considering various factors to ensure it aligns with your specific business needs and goals. This software is designed to provide valuable insights into your IT infrastructure, enabling you to proactively identify and address potential issues before they impact your operations.
Evaluating Software Based on Key Factors
When choosing remote IT monitoring software, it is essential to evaluate it based on several crucial factors. These factors will determine how well the software meets your requirements and contributes to the overall efficiency and security of your IT infrastructure.
- Scalability: The software should be able to scale with your business as it grows. This means it should be able to handle increasing amounts of data and monitor more devices and systems without compromising performance. Look for software that offers flexible pricing plans and can adapt to your changing needs.
- Integration Capabilities: The software should integrate seamlessly with your existing IT systems and tools. This includes integration with your ticketing system, asset management software, and other essential applications. Look for software that offers a wide range of integrations and APIs to ensure compatibility.
- User-friendliness: The software should be easy to use and understand, even for users without extensive technical expertise. Look for a user-friendly interface with clear dashboards, intuitive navigation, and helpful documentation. A user-friendly interface ensures your team can effectively utilize the software and gain valuable insights.
- Cost-effectiveness: The software should provide value for money. Consider the cost of the software, the features it offers, and the potential return on investment. Compare different software solutions and choose the one that best meets your budget and offers the features you need.
Step-by-Step Guide for Choosing Remote IT Monitoring Software
A systematic approach to choosing the right remote IT monitoring software can streamline the process and ensure you make an informed decision.
- Define Your Requirements: Begin by clearly defining your specific needs and objectives. Consider the types of devices and systems you need to monitor, the level of detail required, and the desired reporting capabilities. This will help you narrow down your search and focus on software that aligns with your specific requirements.
- Research and Evaluate Software Options: Explore different remote IT monitoring software solutions available in the market. Read reviews, compare features, and consider the pricing models. This research will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the available options and their strengths and weaknesses.
- Request Demonstrations and Trials: Once you have shortlisted a few potential software solutions, request demonstrations or free trials. This will allow you to experience the software firsthand and evaluate its user-friendliness, features, and overall functionality. This hands-on experience will provide valuable insights into how the software meets your specific needs.
- Consider Security and Compliance: Ensure the software you choose meets your security and compliance requirements. Look for features such as data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with industry standards like HIPAA or GDPR. This is crucial to protect sensitive data and ensure your IT infrastructure remains secure.
- Check Customer Support and Documentation: Evaluate the quality of customer support and documentation provided by the software vendor. Look for responsive support channels, comprehensive documentation, and a strong track record of customer satisfaction. This will ensure you have access to timely assistance and resources when needed.
- Make an Informed Decision: Based on your evaluation, choose the remote IT monitoring software that best meets your requirements, budget, and overall needs. Consider the long-term value and ensure the software is scalable and adaptable to your future business growth.
Implementation and Configuration
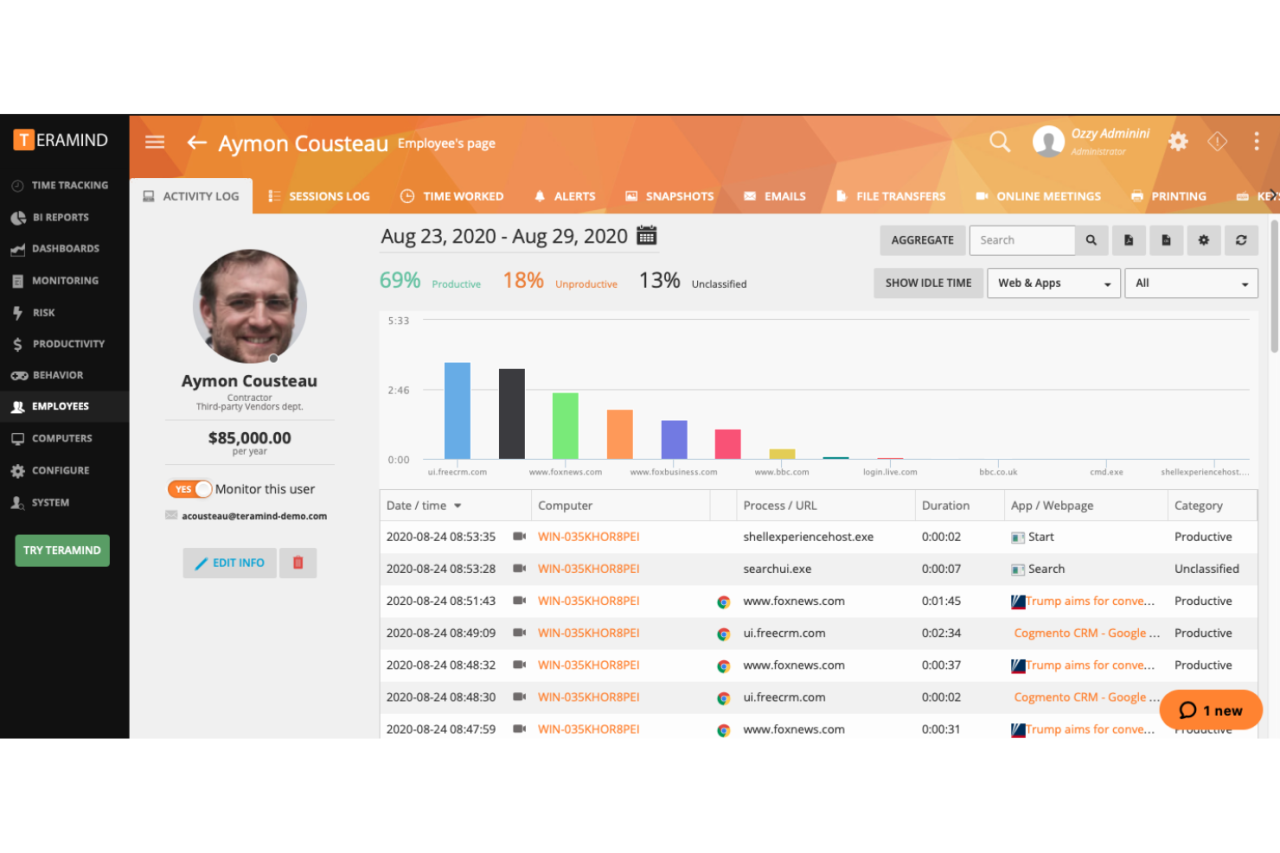
Implementing and configuring remote IT monitoring software involves a series of steps that ensure seamless integration with your existing IT infrastructure. This process requires careful planning and execution to guarantee effective monitoring and management of your systems.
Installing the Software
Installing the software is the first step in the implementation process. The installation process typically involves downloading the software from the vendor’s website, running the installer, and following the on-screen instructions. The installation may require administrative privileges and may involve configuring the software to connect to your network and systems.
Configuring Monitoring Agents, Remote it monitoring software
Monitoring agents are software components that are installed on the devices you want to monitor. These agents collect data about the performance and health of the devices and send it to the central monitoring console. The configuration of monitoring agents involves specifying the type of data to be collected, the frequency of data collection, and the alert thresholds.
- Agent Deployment: Agents can be deployed manually or automatically. Manual deployment involves installing the agent on each device individually. Automatic deployment utilizes tools like agent push or network discovery to install agents on multiple devices simultaneously.
- Data Collection: Configuring data collection involves selecting the metrics and performance indicators that are relevant to your monitoring needs. For example, you may want to monitor CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, network traffic, and application performance.
- Alert Thresholds: Setting alert thresholds involves defining the acceptable limits for various metrics. When a metric exceeds its threshold, the software triggers an alert to notify the IT team.
Setting Up Alerts and Notifications
Alerts and notifications are crucial for proactive IT management. They inform the IT team about potential issues or problems with monitored systems. Setting up alerts and notifications involves configuring the software to send notifications via email, SMS, or other communication channels.
- Alert Triggers: Alerts can be triggered by various events, such as high CPU utilization, low disk space, network connectivity issues, or application errors. The software allows you to define specific triggers for each alert.
- Notification Channels: You can configure the software to send alerts via email, SMS, or other communication channels. This ensures that the IT team receives notifications in a timely manner, regardless of their location.
- Escalation Rules: You can define escalation rules to automatically escalate alerts to higher-level personnel if the issue is not resolved within a specified timeframe. This helps ensure that critical issues are addressed promptly.
Practical Tips for Successful Implementation
Successful implementation of remote IT monitoring software requires careful planning and execution. Here are some practical tips:
- Start Small: Begin by monitoring a few critical systems and gradually expand the scope of monitoring as you gain experience.
- Test Thoroughly: Test the software and its configuration thoroughly before deploying it in production. This helps identify and resolve any potential issues early on.
- Document Everything: Document the configuration of the software, the monitoring agents, and the alerts. This documentation will be helpful for troubleshooting and future maintenance.
- Train Your Team: Train your IT team on how to use the software and interpret the data it provides. This ensures that they can effectively monitor and manage your systems.
- Seek Support: If you encounter any difficulties, don’t hesitate to seek support from the software vendor or a qualified IT consultant. They can provide guidance and assistance with the implementation process.
Monitoring and Analysis
Remote IT monitoring software is the backbone of proactive IT management, providing real-time insights into the health and performance of your infrastructure. It empowers you to stay ahead of potential issues, minimize downtime, and optimize system efficiency.
Real-time Monitoring of IT Infrastructure
Real-time monitoring is the cornerstone of effective IT management. Remote IT monitoring software continuously collects data from various sources within your IT infrastructure, such as servers, networks, applications, and devices. This data is then processed and presented in a user-friendly interface, providing a comprehensive overview of the current state of your systems.
Analyzing Performance Data and Identifying Potential Issues
The collected performance data is not just raw information; it’s a treasure trove of insights that can be analyzed to identify potential issues before they become critical. By comparing current data against historical trends and predefined thresholds, the software can detect anomalies and alert you to potential problems. These alerts can be configured to trigger based on specific parameters, such as CPU utilization exceeding a certain limit, disk space nearing capacity, or network latency exceeding a threshold.
Utilizing Reports and Dashboards
Reports and dashboards provide a powerful means of visualizing and analyzing the collected data. They offer a consolidated view of system health and performance, enabling you to identify trends, patterns, and areas requiring attention. Reports can be customized to focus on specific metrics, devices, or time periods, providing tailored insights for different stakeholders.
Integration with Other Tools: Remote It Monitoring Software
Remote IT monitoring software can significantly enhance its capabilities and streamline workflows by integrating with other tools. This integration fosters a more comprehensive and collaborative approach to IT management, allowing for efficient data sharing, automated actions, and a unified view of IT operations.
Integration with Ticketing Systems
Integrating remote IT monitoring software with ticketing systems, such as Zendesk, Jira, or ServiceNow, creates a seamless workflow for incident management. When an alert is triggered by the monitoring software, it can automatically create a ticket within the ticketing system, providing detailed information about the issue, including the affected device, the nature of the problem, and relevant logs.
- Improved Incident Response: Automating ticket creation eliminates manual steps and ensures prompt incident response, minimizing downtime and improving overall efficiency.
- Centralized Incident Management: All incidents are tracked and managed within the ticketing system, providing a central repository for incident history, resolution details, and communication logs.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Integration enables seamless collaboration between IT support teams, allowing them to work together efficiently to resolve issues.
Integration with Collaboration Platforms
Integrating remote IT monitoring software with collaboration platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Google Chat enables real-time communication and collaboration within IT teams.
Remote IT monitoring software is a vital tool for keeping an eye on your systems, ensuring everything runs smoothly. A key aspect of this software is the ability to analyze data, and for this, the R programming language is often a go-to choice.
Its powerful statistical capabilities and data visualization tools make it ideal for understanding complex IT monitoring data and identifying potential issues before they become major problems.
- Real-Time Notifications: Alerts can be sent directly to team channels, ensuring that all relevant personnel are notified immediately of any issues.
- Streamlined Communication: Discussions and troubleshooting can occur within the collaboration platform, fostering efficient communication and information sharing.
- Enhanced Visibility: Integrations provide a centralized platform for monitoring and collaboration, allowing for greater transparency and visibility into IT operations.
Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
Integrating remote IT monitoring software with SIEM systems, such as Splunk, LogRhythm, or AlienVault, allows for a more comprehensive security posture by correlating monitoring data with security events.
- Enhanced Threat Detection: By combining monitoring data with security logs, SIEM systems can identify potential security threats that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Automated Security Responses: Integrations can trigger automated security responses, such as blocking access or isolating infected devices, based on pre-defined rules.
- Improved Incident Investigation: SIEM systems can provide valuable insights into security incidents, aiding in the investigation and remediation process.
Future Trends in Remote IT Monitoring
The landscape of remote IT monitoring is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Several key trends are shaping the future of this crucial aspect of IT management.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are poised to revolutionize remote IT monitoring by automating tasks, enhancing predictive capabilities, and improving overall efficiency.
- Automated Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various IT systems to identify unusual patterns and potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach reduces downtime and improves system stability.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data and real-time metrics, AI models can predict when equipment is likely to fail, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of unexpected outages.
- Personalized Insights: AI-powered dashboards can provide tailored insights and recommendations based on individual system configurations and user preferences, helping IT teams make informed decisions and optimize performance.
Cloud-Native Technologies
The increasing adoption of cloud-native technologies is driving a shift towards cloud-based remote IT monitoring solutions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based solutions offer unmatched scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to easily adjust monitoring capabilities as their needs evolve.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based models often provide a more cost-effective alternative to traditional on-premises solutions, reducing upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Integration with Cloud Services: Cloud-based monitoring tools seamlessly integrate with other cloud services, enabling comprehensive visibility across the entire IT infrastructure, from on-premises to cloud environments.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The growing adoption of IoT devices is creating new challenges and opportunities for remote IT monitoring.
- Expanding Monitoring Scope: IoT devices generate a vast amount of data, requiring advanced monitoring tools capable of collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data from diverse sources.
- Security Considerations: The increasing number of connected devices raises concerns about security vulnerabilities, necessitating robust monitoring solutions that can detect and respond to security threats in real time.
- Performance Optimization: IoT devices often operate in resource-constrained environments, demanding efficient monitoring tools that minimize network bandwidth consumption and optimize device performance.
Outcome Summary

As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation and rely heavily on their IT infrastructure, the importance of remote IT monitoring software will only grow. By leveraging the insights and best practices Artikeld in this guide, organizations can effectively optimize their IT operations, ensure business continuity, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
