Remote device monitoring software has revolutionized the way businesses manage and optimize their technology assets. This powerful software enables organizations to gain real-time visibility into the performance, health, and security of their devices, from desktops and laptops to servers and mobile devices. By providing a centralized platform for data collection, analysis, and reporting, remote device monitoring software empowers IT professionals to proactively identify and address potential issues, improve system efficiency, and enhance overall security.
Table of Contents
Whether you’re a small business owner or a large enterprise, remote device monitoring software can offer significant benefits. Imagine being able to remotely monitor the performance of your servers, identify security threats before they escalate, and optimize resource allocation for greater efficiency. This software provides the tools and insights needed to make informed decisions and ensure the smooth operation of your technology infrastructure.
Introduction to Remote Device Monitoring Software
Remote device monitoring software, often referred to as remote monitoring and management (RMM) software, empowers businesses to oversee and manage their IT infrastructure remotely. It provides a centralized platform for monitoring the health, performance, and security of devices, such as computers, servers, and network equipment, regardless of their physical location.
This software acts as a virtual IT department, enabling businesses to gain real-time insights into their technology environment. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, it provides comprehensive visibility into the performance and security of their devices.
Real-World Applications of Remote Device Monitoring Software
Remote device monitoring software finds widespread use across various industries, helping businesses streamline their operations and enhance their IT infrastructure. Here are some examples:
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics rely on remote device monitoring software to ensure the smooth functioning of critical medical equipment, such as imaging machines, patient monitoring systems, and laboratory instruments. This helps them maintain patient safety and improve healthcare delivery.
- Finance: Financial institutions leverage remote device monitoring software to protect sensitive data and ensure the security of their networks. It enables them to monitor network traffic, detect suspicious activities, and respond swiftly to security threats.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing companies utilize remote device monitoring software to optimize production processes and minimize downtime. It allows them to track machine performance, identify potential issues, and schedule maintenance proactively.
- Education: Educational institutions use remote device monitoring software to manage their computer labs and ensure the smooth operation of student devices. It facilitates troubleshooting, software updates, and security measures for a secure and efficient learning environment.
Benefits of Implementing Remote Device Monitoring Software
Implementing remote device monitoring software brings numerous advantages to businesses, including:
- Improved IT Efficiency: By automating tasks like software updates, patch management, and security checks, remote device monitoring software frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. This significantly enhances overall IT efficiency.
- Enhanced Security: Remote device monitoring software provides real-time security alerts and proactive threat detection. It enables businesses to identify and respond to security breaches quickly, minimizing potential damage and protecting sensitive data.
- Reduced Downtime: Proactive monitoring and maintenance capabilities help prevent downtime by identifying potential issues before they escalate. This ensures continuous operations and minimizes disruptions to business activities.
- Cost Savings: Remote device monitoring software eliminates the need for on-site IT support, reducing travel expenses and the need for large IT teams. This translates into significant cost savings for businesses.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: With remote device monitoring software, businesses can provide faster and more efficient support to their customers. This enhances customer satisfaction and strengthens relationships.
Benefits of Using Remote Device Monitoring Software
Remote device monitoring software offers a plethora of benefits that can significantly improve business operations and enhance overall efficiency. By providing real-time insights into the performance and health of devices, this software empowers organizations to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and proactively address potential issues.
Improved Productivity
Remote device monitoring software can significantly boost productivity by enabling businesses to identify and address performance bottlenecks in real-time. By monitoring key metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk space, IT teams can quickly identify devices that are struggling to keep up with demands. This allows them to proactively allocate resources, optimize system configurations, and prevent performance issues from impacting end-users.
Enhanced Security
Remote device monitoring software plays a crucial role in bolstering security by providing a comprehensive view of network activity and user behavior. This enables organizations to detect and respond to potential security threats in real-time. For example, the software can monitor for suspicious login attempts, unauthorized access, and data breaches, allowing security teams to take immediate action to mitigate risks.
Reduced Downtime
Downtime can be incredibly costly for businesses, disrupting operations and impacting productivity. Remote device monitoring software helps minimize downtime by providing early warning signs of potential issues. By monitoring system performance, hardware health, and application availability, IT teams can proactively identify and address problems before they escalate into major outages.
Optimized Resource Allocation
Remote device monitoring software enables businesses to optimize resource allocation by providing insights into device utilization. By analyzing data on CPU usage, memory consumption, and network bandwidth, IT teams can identify underutilized resources and reallocate them to areas where they are needed most. This ensures that resources are used efficiently, maximizing performance and minimizing costs.
“Remote device monitoring software empowers businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their IT infrastructure, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that improve efficiency, enhance security, and minimize downtime.”
Implementation and Configuration
Implementing and configuring remote device monitoring software involves a series of steps that ensure seamless integration with your existing network infrastructure and user environment. This process requires careful consideration of technical aspects, including network infrastructure, user permissions, and data security protocols, to ensure a secure and efficient monitoring solution.
Network Infrastructure
The network infrastructure plays a crucial role in remote device monitoring. Understanding the network topology, bandwidth, and latency is essential for choosing the right software and ensuring optimal performance.
- Network Topology: Determine the network layout, including the number of devices, network segments, and routing protocols. This helps in selecting the appropriate monitoring software that can effectively manage the network.
- Bandwidth: Evaluate the available bandwidth to handle the data generated by the monitoring software. Insufficient bandwidth can lead to performance issues, particularly when monitoring a large number of devices.
- Latency: Consider the latency between the monitoring server and the monitored devices. High latency can affect real-time monitoring capabilities and response times.
User Permissions
Defining user permissions is essential for controlling access to the monitoring software and the data it collects. Implementing a robust permission system ensures data security and prevents unauthorized access.
- Role-Based Access Control: Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to assign different levels of access to different users based on their roles within the organization. For example, administrators may have full access to all data and settings, while regular users may only have access to specific devices or data points.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) to enhance security by requiring users to provide two forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, before accessing the monitoring software.
- Auditing: Implement auditing capabilities to track user activity and identify potential security breaches. This helps in detecting unauthorized access and identifying any malicious actions.
Data Security Protocols
Data security is paramount when implementing remote device monitoring software. Implementing robust protocols ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the collected data.
- Encryption: Use encryption to protect data in transit and at rest. Encrypting data prevents unauthorized access and ensures data confidentiality.
- Secure Protocols: Use secure protocols like HTTPS and SSH to communicate between the monitoring server and the monitored devices. These protocols encrypt data and prevent eavesdropping or data interception.
- Data Retention Policies: Establish clear data retention policies to determine how long data is stored and how it is disposed of. This helps comply with data privacy regulations and minimize security risks.
Security Considerations
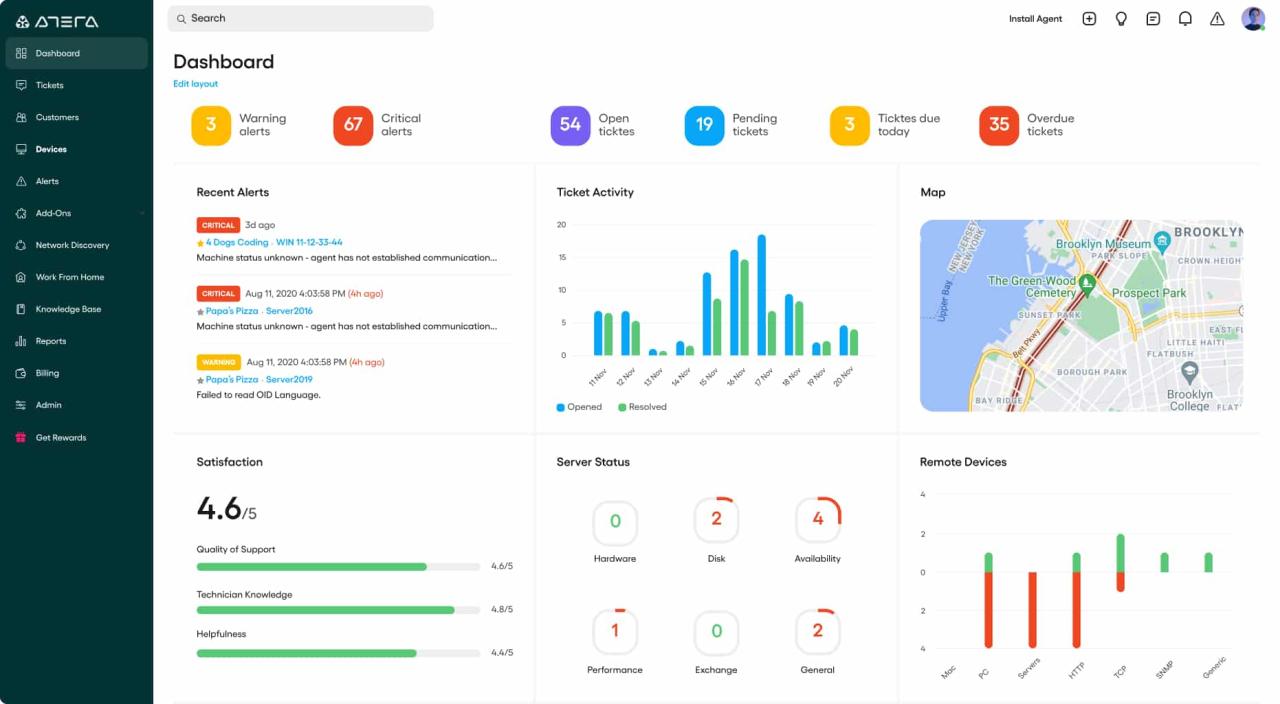
Remote device monitoring software offers significant advantages, but its use also presents unique security challenges. It’s crucial to understand these challenges and implement appropriate safeguards to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of your systems.
Data Security and Privacy
Data collected by remote device monitoring software can include sensitive information, such as user activity logs, network traffic, and device configurations. This data must be protected from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Data Encryption: Implement robust encryption protocols to secure data both during transmission and storage. Encrypt data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access. For example, using Transport Layer Security (TLS) for secure communication and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for data encryption at rest.
- Access Control: Implement strict access control measures to restrict access to collected data only to authorized personnel. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign specific permissions to users based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Data Retention Policies: Establish clear data retention policies to determine how long data is stored and when it should be deleted. This helps minimize the risk of data breaches and comply with privacy regulations.
- Data Anonymization: Consider anonymizing data whenever possible to protect user privacy. Remove personally identifiable information (PII) from collected data unless it’s absolutely necessary for monitoring purposes.
Vulnerability Management
Remote device monitoring software itself can be vulnerable to security threats, such as malware infections, unauthorized access, or data leaks.
- Software Updates: Regularly update the remote device monitoring software to patch vulnerabilities and improve security. Implement automated update mechanisms to ensure timely patching.
- Secure Authentication: Use strong authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access to the monitoring software. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for an extra layer of security.
- Network Security: Secure the network infrastructure used for remote monitoring. Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to detect and prevent malicious activity.
Risk Mitigation
It’s important to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks associated with remote device monitoring software.
- Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in the monitoring system.
- Security Awareness Training: Provide security awareness training to users who have access to the monitoring software. Educate them on best practices for data security and password management.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to handle security incidents promptly and effectively. This plan should include steps for containment, remediation, and reporting.
Legal and Ethical Implications: Remote Device Monitoring Software
Remote device monitoring software, while offering significant benefits for businesses, also raises critical legal and ethical concerns that require careful consideration. It’s crucial to understand the potential impact on employee privacy, data ownership, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Employee Privacy
Employee privacy is a paramount concern when implementing remote device monitoring software. Employers must strike a delicate balance between monitoring employee activity and respecting their right to privacy.
- Transparency and Consent: Employers should clearly communicate their monitoring policies to employees, outlining the types of data collected, the purpose of monitoring, and the extent of employee access to their own data. Obtaining informed consent from employees before implementing monitoring is essential.
- Data Minimization: Employers should only collect data that is strictly necessary for legitimate business purposes. This includes avoiding the collection of personal information that is irrelevant to work performance, such as browsing history or personal emails.
- Reasonable Expectations of Privacy: Employees have a reasonable expectation of privacy in their personal communications and activities, even when using company devices. Monitoring should be limited to work-related activities and should not intrude on personal matters.
- Data Retention: Employers should establish clear data retention policies, specifying how long they will retain employee data and the procedures for data deletion.
Data Ownership, Remote device monitoring software
The ownership of data collected through remote device monitoring can be a complex issue.
- Employee Data: While employees may be using company devices, the data generated through their activities, including emails, documents, and browsing history, may contain personal information. Employers should clarify ownership rights and ensure employees understand how their data is used and protected.
- Company Data: Data related to company operations, such as customer information, financial records, and intellectual property, is typically owned by the employer. However, employee data generated during work activities can raise questions about ownership.
- Data Security: Employers are responsible for securing all data collected through remote device monitoring. This includes implementing robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and data loss.
Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with relevant regulations is essential when using remote device monitoring software.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): The GDPR, which applies to organizations processing personal data of individuals in the European Union, requires organizations to obtain explicit consent for data processing, ensure data security, and provide individuals with the right to access, rectify, and erase their data.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): The CCPA, which applies to businesses that collect personal information of California residents, grants consumers the right to access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their data. Organizations must comply with these rights and ensure data security.
- Other Regional Regulations: Many other jurisdictions have specific regulations governing data privacy and employee monitoring. Employers must comply with all applicable regulations to avoid legal penalties and maintain ethical practices.
Best Practices for Ethical Use
Ensuring ethical and responsible use of remote device monitoring software is crucial.
- Clear Purpose and Scope: Define the specific purpose and scope of monitoring, ensuring it is aligned with legitimate business needs and avoids unnecessary intrusion into employee privacy.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data that is absolutely necessary for the intended purpose and avoid collecting unnecessary personal information.
- Transparency and Communication: Communicate monitoring policies clearly and transparently to employees, providing them with information about the types of data collected, the purpose of monitoring, and their rights regarding their data.
- Employee Training: Provide employees with training on data privacy and security, highlighting their responsibilities and the importance of protecting sensitive information.
- Regular Review and Updates: Regularly review and update monitoring policies to ensure they remain aligned with best practices, legal requirements, and evolving employee expectations.
Future Trends in Remote Device Monitoring

The field of remote device monitoring is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing reliance on connected devices. Emerging trends are shaping the future of remote device monitoring, leading to enhanced capabilities, new applications, and a more sophisticated approach to managing and securing connected devices.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing remote device monitoring by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and providing insights that were previously impossible. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from connected devices, identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate potential issues. This allows for proactive maintenance and early detection of problems, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze historical data from devices to predict when maintenance is needed, preventing unexpected failures and reducing downtime. For example, in a manufacturing setting, AI can analyze sensor data from machines to predict when a part is likely to fail, allowing for scheduled maintenance before the failure occurs.
- Anomaly Detection: AI can identify unusual patterns in device data that may indicate a security breach or malfunction. This can help security teams quickly respond to threats and prevent data breaches. For instance, an AI system could detect unusual network traffic patterns or changes in device behavior that could indicate a malware infection.
- Performance Optimization: AI can optimize device performance by analyzing data and adjusting settings in real-time. For example, an AI system could optimize the energy consumption of a data center by adjusting the cooling systems based on real-time temperature and workload data.
Cloud Computing and Remote Device Monitoring
Cloud computing is playing a significant role in the growth of remote device monitoring. Cloud-based platforms provide a scalable and cost-effective infrastructure for storing, processing, and analyzing data from connected devices. This allows businesses to access and manage their devices from anywhere in the world, without the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud platforms offer a high degree of scalability, allowing businesses to easily add or remove devices as needed. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with rapidly growing device fleets.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-based solutions can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises solutions, as businesses only pay for the resources they use. This can be a significant advantage for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Data Security and Compliance: Cloud providers typically offer robust security measures to protect data and ensure compliance with industry regulations. This can be a significant advantage for businesses that handle sensitive data.
Future Applications and Use Cases
Remote device monitoring is becoming increasingly ubiquitous, with applications extending beyond traditional IT infrastructure management. The integration of AI, ML, and cloud computing is opening up new possibilities for remote device monitoring in various industries.
- Smart Cities: Remote device monitoring is playing a critical role in the development of smart cities. Sensors deployed throughout cities can collect data on traffic flow, air quality, and other environmental factors. This data can be used to optimize city services, improve transportation, and enhance public safety. For example, sensors in traffic lights can adjust timing based on real-time traffic conditions, reducing congestion and improving traffic flow.
- Healthcare: Remote device monitoring is transforming healthcare by enabling remote patient monitoring and diagnosis. Wearable devices and medical sensors can collect data on vital signs, medication adherence, and other health indicators. This data can be transmitted to healthcare providers, allowing them to monitor patients remotely and intervene early in case of health issues. For example, a patient with heart disease can wear a device that monitors their heart rate and transmits the data to their doctor, enabling early detection of potential problems.
- Agriculture: Remote device monitoring is improving agricultural efficiency and sustainability. Sensors can monitor soil moisture, temperature, and other environmental factors, providing farmers with real-time insights into crop health and irrigation needs. This data can help farmers optimize resource use and improve crop yields. For example, sensors in a field can monitor soil moisture levels and automatically adjust irrigation systems to ensure optimal water use.
Wrap-Up
Remote device monitoring software has emerged as an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to optimize their technology infrastructure, enhance security, and improve overall efficiency. By providing real-time insights, proactive alerts, and robust reporting capabilities, this software empowers IT professionals to make data-driven decisions and maintain a secure and reliable technology environment. As technology continues to evolve, remote device monitoring will play an increasingly vital role in ensuring the smooth operation and security of our connected world.
Remote device monitoring software can be a powerful tool for businesses, allowing them to track activity, troubleshoot issues, and ensure security. For those who prefer the traditional format of PDFs, converting EPUB files to PDF is a simple task with a tool like epub to pdf converter.
Once converted, these PDFs can then be easily integrated into remote device monitoring reports for a comprehensive overview of system performance and user behavior.
