PDF to DWG converter opens a door to seamless collaboration between designers, architects, and engineers. This conversion process allows for the effortless transformation of PDF files, often used for sharing blueprints and designs, into the industry-standard DWG format, which is favored by AutoCAD and other CAD software. This bridge between formats facilitates smoother workflows, enhances communication, and streamlines project execution.
Table of Contents
Understanding the intricacies of both PDF and DWG formats is crucial to achieving accurate and efficient conversions. PDF, known for its versatility and cross-platform compatibility, excels at preserving document layouts and ensuring visual fidelity. Conversely, DWG is the cornerstone of CAD applications, providing a highly detailed and editable environment for creating and manipulating technical drawings.
Understanding PDF and DWG Formats
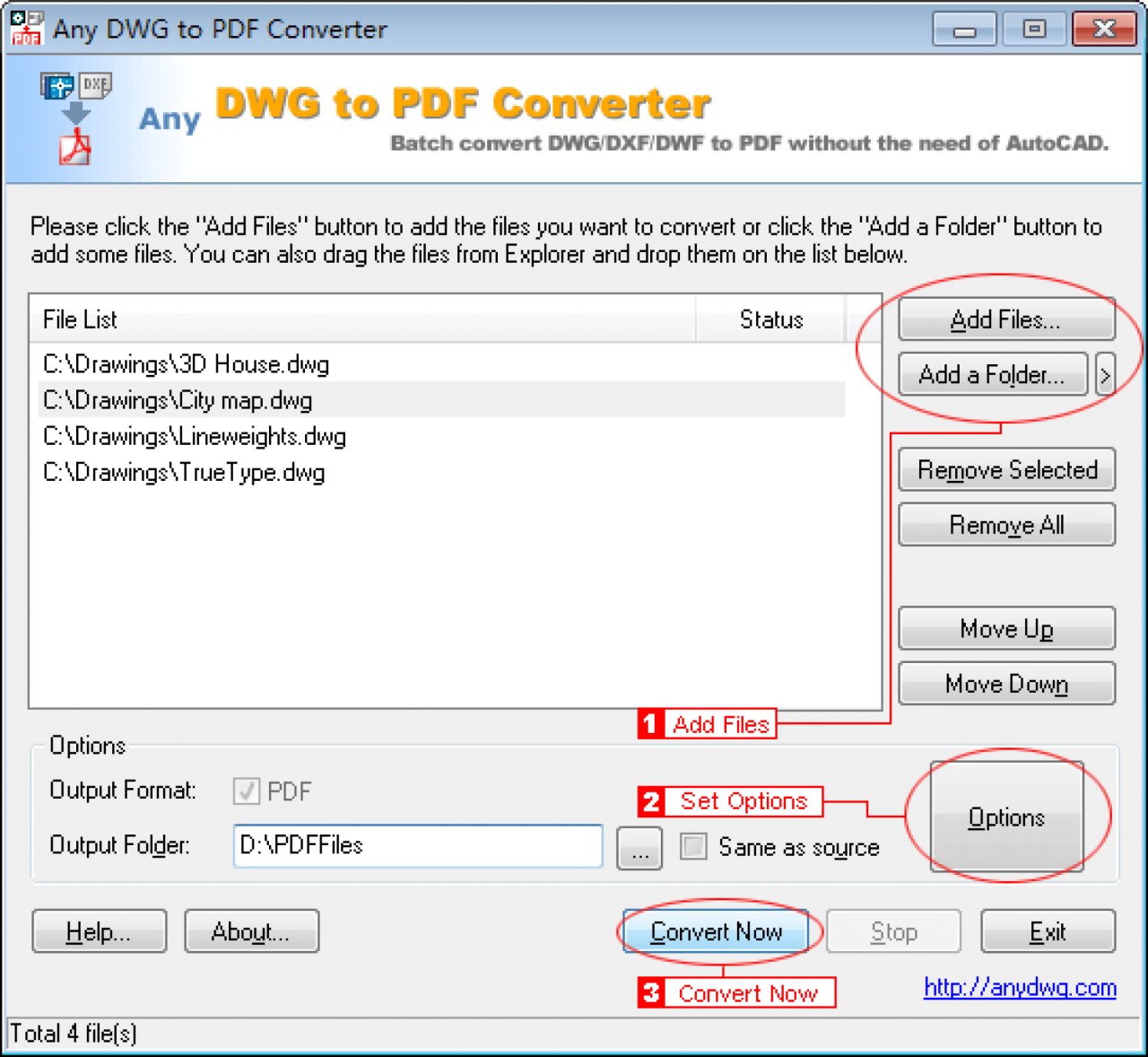
This section will delve into the characteristics of PDF and DWG formats, highlighting their key differences and similarities. Understanding these formats is crucial for efficient file conversion and data exchange between various applications.
PDF Format
PDF, which stands for Portable Document Format, is a file format developed by Adobe Systems. It is designed to ensure that documents appear the same on any computer, regardless of the operating system, software, or hardware used to view them. This is achieved by embedding all the necessary fonts, images, and other elements within the PDF file.
Here are some key characteristics of the PDF format:
- Cross-platform compatibility: PDFs can be viewed and printed on virtually any computer, making them suitable for sharing and distribution.
- High fidelity: PDFs preserve the original formatting and layout of documents, ensuring that they appear as intended.
- Security features: PDFs can be password-protected, limiting access and preventing unauthorized modifications.
- Searchable text: PDFs can contain embedded text that can be searched, making it easy to find specific information within the document.
- Multimedia support: PDFs can incorporate various multimedia elements, such as images, videos, and audio files.
DWG Format
DWG, which stands for Drawing, is a proprietary file format developed by Autodesk. It is primarily used for storing and exchanging two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) design data, primarily for computer-aided design (CAD) applications.
Here are some key characteristics of the DWG format:
- Vector-based graphics: DWG files use vectors to represent geometric shapes, allowing for high-quality scaling and resizing without loss of detail.
- Object-oriented design: DWG files store design elements as objects, allowing for easy manipulation and modification.
- Layer management: DWG files support the organization of design elements into layers, simplifying the design process and enabling efficient collaboration.
- Metadata support: DWG files can store metadata, such as design specifications, project details, and other relevant information.
- Industry-standard format: DWG is widely used in various industries, making it a common file format for exchanging design data.
Comparison of PDF and DWG Formats
PDF and DWG formats serve distinct purposes and have different strengths and limitations. While PDFs are designed for document viewing and distribution, DWG files are primarily used for design and engineering applications.
Here’s a table comparing key features of PDF and DWG formats:
| Feature | DWG | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Document viewing and distribution | Design and engineering |
| Data type | Text, images, multimedia | Geometric shapes, objects, layers |
| Scalability | Raster-based, can lose detail when scaled | Vector-based, scalable without loss of detail |
| Editability | Limited editing capabilities | Highly editable, designed for design modifications |
| Industry use | Widely used across various industries | Primarily used in design and engineering fields |
Accuracy and Quality of Conversion
Converting a PDF to a DWG file is a complex process that involves transforming data from one format to another. While various converters exist, the accuracy and quality of the conversion can vary significantly. Several factors contribute to this variability, and understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about the conversion process.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
The accuracy of a PDF to DWG conversion depends on various factors. These include:
- The complexity of the PDF: A PDF containing simple text and basic shapes is easier to convert than a complex PDF with multiple layers, embedded images, and advanced formatting.
- The DWG version: Different versions of the DWG format have different capabilities. Converting a PDF to an older DWG version may result in a loss of information.
- The quality of the PDF: A high-quality PDF with well-defined shapes and clear text is more likely to convert accurately than a low-quality PDF with blurry images or distorted text.
- The converter software: Different PDF to DWG converters use varying algorithms and approaches, leading to differences in accuracy and output quality.
Potential Loss of Information
During conversion, some information might be lost or transformed. This can include:
- Formatting: Text formatting, such as font styles, sizes, and colors, may not be preserved during conversion.
- Images: Images embedded in the PDF might not be converted accurately, leading to a loss of resolution or color fidelity.
- Layers: If the PDF has multiple layers, they may not be preserved in the DWG file, or the conversion might combine them into a single layer.
- Annotations: Annotations, such as comments or highlights, may not be converted or might be lost during the conversion process.
Conversion of Complex Layouts and Content
Different PDF to DWG converters handle complex layouts and content differently. Some converters might excel at converting specific types of content, while others might struggle with particular elements. For example:
- Vector graphics: Some converters can accurately convert vector graphics, preserving their original quality and detail. Others might convert them as raster images, resulting in a loss of resolution.
- Text: While most converters can convert text, some might not handle complex text formatting or languages correctly.
- 3D objects: Converting 3D objects from a PDF to a DWG can be challenging, and some converters might not support this feature at all.
Considerations for Choosing a Converter
Selecting the right PDF to DWG converter involves considering various factors to ensure accurate and efficient conversion. The choice depends on specific needs and the complexity of the conversion task.
File Size
The size of the PDF file is a crucial factor influencing conversion speed and resource consumption. Large PDF files can require more processing power and time, potentially affecting the efficiency of the conversion process.
Accuracy
The accuracy of the conversion is paramount, ensuring that the resulting DWG file maintains the integrity of the original PDF content. This includes preserving geometric shapes, text, and other design elements.
Features
Various PDF to DWG converters offer different features, catering to specific needs. Some key features include:
- Batch conversion: Allows for simultaneous conversion of multiple PDF files.
- Customization options: Enable users to adjust settings like line thickness, color, and layer assignments.
- Support for different DWG versions: Ensures compatibility with various AutoCAD versions.
- Advanced features: Some converters may offer additional features like vectorization, object recognition, and image processing.
Cost
The cost of the converter can vary significantly depending on the features, licensing options, and vendor. Free converters may offer limited functionality, while paid options provide advanced features and support.
Recommendations
For basic conversion needs, free online converters can be a suitable option. However, for more complex conversions requiring accuracy, advanced features, and support, paid converters are recommended.
Future Trends in Conversion Technology
The field of PDF to DWG conversion is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for seamless data exchange between different design and engineering applications. This evolution is paving the way for more efficient, accurate, and user-friendly conversion processes.
Emerging Technologies and Advancements
The future of PDF to DWG conversion is poised for significant advancements, with emerging technologies playing a crucial role in enhancing accuracy, speed, and functionality.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming the conversion process by automating complex tasks and improving accuracy. AI algorithms can analyze PDF content and identify objects, text, and geometric shapes, enabling more precise conversion to DWG format. ML models can learn from past conversions and adapt to different PDF structures, ensuring consistent and reliable results. For example, AI-powered conversion tools can automatically detect and extract specific design elements from PDF files, such as lines, curves, and text, resulting in more accurate DWG representations.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based conversion services offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. By leveraging cloud infrastructure, users can access powerful conversion tools and resources without the need for local software installations. Cloud-based platforms also enable collaborative workflows, allowing multiple users to work on conversion projects simultaneously. For instance, a cloud-based PDF to DWG converter can handle large files and complex drawings, ensuring faster processing times and improved efficiency.
- Advanced Image Processing Techniques: The conversion process relies heavily on image processing techniques to accurately interpret and translate PDF content into DWG format. Advancements in image processing, such as improved image recognition and segmentation algorithms, are enhancing the quality and accuracy of conversions. For example, using sophisticated image analysis techniques, conversion tools can accurately identify and convert different types of lines, curves, and shapes, resulting in more detailed and precise DWG drawings.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Converting PDF files to DWG format involves handling sensitive data, making security and privacy paramount. It’s crucial to understand the potential risks and take necessary precautions to protect your information.
Data Security During Conversion, Pdf to dwg converter
Using PDF to DWG converters introduces potential security risks. The process involves transferring data between different applications, potentially exposing it to unauthorized access or manipulation.
It’s essential to use reputable converters that implement robust security measures. These measures should include:
- Data Encryption: Ensure the converter encrypts data during transmission and storage, preventing unauthorized access. Look for converters that support industry-standard encryption protocols like AES-256.
- Secure Communication Channels: The converter should utilize secure protocols like HTTPS for data transfer, safeguarding information from interception or tampering.
- Regular Security Updates: Ensure the converter is regularly updated with security patches to address vulnerabilities and prevent exploits.
Protecting Sensitive Information
Before converting PDF files, consider the following steps to protect sensitive information:
- Remove Sensitive Data: If possible, remove or redact sensitive information from the PDF file before conversion. This reduces the risk of exposure during the process.
- Use Watermarks: Consider adding watermarks to the DWG file to identify its origin and prevent unauthorized distribution.
- Restrict Access: Implement access control measures on the DWG file to limit access to authorized individuals.
- Password Protection: Consider password-protecting the DWG file to prevent unauthorized access and modification.
Best Practices for Using PDF to DWG Converters
Maximizing the accuracy and efficiency of your PDF to DWG conversions requires understanding and applying best practices. These practices are essential for achieving the desired results, especially when dealing with complex or specialized PDF files.
Optimizing Conversion Results
Optimizing your PDF to DWG conversions involves a series of steps that can significantly improve the accuracy and quality of the output. These steps ensure that the converted DWG file maintains the integrity and fidelity of the original PDF content.
- Choose the Right Converter: Selecting a converter specifically designed for your needs is crucial. Consider the type of PDF files you’ll be converting, the desired output format, and any specific features you require, such as batch processing or advanced editing capabilities.
- Pre-process Your PDF: Before conversion, ensure your PDF file is optimized for conversion. This might involve simplifying the file structure, removing unnecessary elements, or adjusting the file size. This step enhances conversion speed and reduces potential errors.
- Define Conversion Settings: Most converters offer various settings that control the conversion process. Carefully select the appropriate settings based on your specific needs, such as the desired output format, resolution, and color depth. These settings directly influence the quality and accuracy of the converted DWG file.
- Test and Refine: After conversion, it’s essential to test the output DWG file to ensure it meets your expectations. This includes verifying the accuracy of lines, curves, text, and other elements. If necessary, adjust the conversion settings or pre-process the PDF further to achieve optimal results.
Handling Different PDF File Types
Different types of PDF files present unique challenges for conversion. Understanding these challenges allows you to choose the right approach and optimize the conversion process for each specific file type.
- Scanned PDFs: Scanned PDFs are images of printed documents, making them difficult to convert accurately. However, using specialized OCR (Optical Character Recognition) software can extract text and convert it into editable DWG elements.
- Vector PDFs: Vector PDFs, created using drawing software, are generally easier to convert. They consist of geometric shapes and lines that can be readily translated into DWG elements. However, ensuring accurate conversion of text and complex shapes may require additional settings or post-processing.
- Mixed PDFs: PDFs containing a combination of text, images, and vector graphics require a more nuanced approach. The converter should be able to handle each element type separately and ensure proper conversion. This might involve using specific settings or adjusting the output format to accommodate different elements.
Ensuring Accurate and Efficient Conversion
Accuracy and efficiency are paramount when converting PDF to DWG files. Implementing strategies to achieve these goals is crucial for maximizing the value of the converted DWG file.
- Verify File Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen converter supports the specific PDF version and features you need. This ensures compatibility and avoids potential conversion errors. Consider using a converter with a wide range of supported file types and features.
- Utilize Batch Conversion: For multiple PDF files, utilize batch conversion features to streamline the process. This saves time and effort, allowing you to convert large volumes of files efficiently.
- Optimize for CAD Software: Choose a converter that outputs DWG files compatible with your specific CAD software. This ensures seamless integration and eliminates compatibility issues.
Last Recap

The ability to convert PDF files to DWG opens a world of possibilities for professionals across various industries. From construction and engineering to architecture and manufacturing, this conversion process empowers users to leverage the strengths of both formats, ensuring efficient collaboration, improved accuracy, and enhanced design workflows. The ongoing evolution of conversion technologies promises even greater efficiency and accuracy in the future, further solidifying the importance of PDF to DWG conversion in today’s digital landscape.
Converting PDFs to DWGs can be a hassle, especially when you need to incorporate the data into a larger project. But if you’re working with a robust system like erpnext , you can streamline this process by integrating the conversion tool directly into your workflow.
This way, you can focus on the bigger picture and let the software handle the technical details, ultimately saving you time and effort.
