Microsoft Office email sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a world where communication thrives. It’s a platform that has become an indispensable tool for individuals and businesses alike, facilitating seamless interaction and fostering connections across the globe.
Table of Contents
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Microsoft Office email, exploring its evolution, features, and applications. We’ll navigate the various types of accounts, delve into the process of setup and configuration, and unravel the secrets of sending, receiving, and managing emails with ease. We’ll also address crucial aspects of security, privacy, and collaboration, ensuring that you have the knowledge and skills to harness the full potential of this powerful communication tool.
Types of Microsoft Office Email Accounts
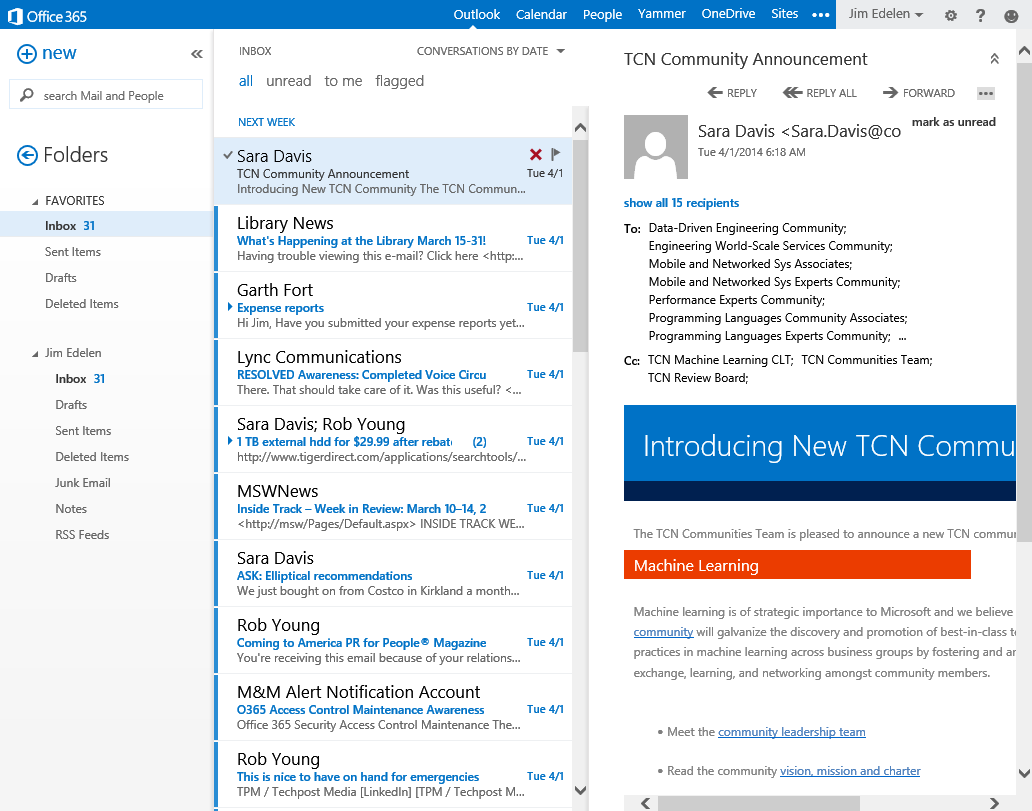
Microsoft Office offers various email accounts, each catering to different needs and purposes. These accounts provide access to features like email, calendar, contacts, and file storage, with varying levels of functionality and accessibility depending on the account type.
Personal Accounts
Personal accounts, such as Outlook.com, are free and readily available to anyone. They are primarily designed for individual use, offering a convenient way to manage emails, contacts, and calendars.
- Free to use: No subscription fees are required to create and use a personal account.
- Basic features: Personal accounts offer essential email functionality, calendar management, and contact storage.
- Limited storage: Free accounts typically have limited storage space for emails, files, and other data.
- Ad-supported: Personal accounts may display advertisements within the email interface.
Business Accounts
Business accounts, such as Microsoft 365, are designed for organizations and businesses. They offer a comprehensive suite of features, including email, collaboration tools, and security measures, tailored for professional use.
- Enhanced features: Business accounts provide advanced email functionality, collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams, and enhanced security features.
- Custom domains: Businesses can use their own domain names for email addresses, creating a professional and branded identity.
- Increased storage: Business accounts offer larger storage capacity for emails, files, and other data.
- Advanced security: Business accounts include features like data encryption, spam filtering, and malware protection.
- Support and administration: Business accounts often include technical support and administrative tools for managing users and accounts.
Educational Accounts
Educational accounts, such as Office 365 Education, are specifically designed for students and educators. They provide access to Microsoft Office applications and email services tailored for academic purposes.
- Free for students and educators: Educational accounts are typically free for eligible students and teachers.
- Access to educational resources: Educational accounts often provide access to educational resources, such as online courses and collaboration tools.
- Collaboration tools: Educational accounts include tools for collaboration, such as OneDrive for file sharing and Microsoft Teams for online meetings.
- Security and privacy: Educational accounts are designed with security and privacy measures in mind to protect student data.
Sending and Receiving Emails: Microsoft Office Email
Microsoft Office email applications provide a user-friendly interface for sending and receiving emails. The process involves composing, sending, and receiving messages, managing drafts, organizing emails in folders, and utilizing search functions for efficient communication.
Composing and Sending Emails
The process of composing and sending emails involves creating a new message, adding recipients, crafting the message body, and sending the email. To compose an email, open the email application and click on the “New Email” button. This will open a new message window where you can enter the recipient’s email address in the “To” field, add a subject line in the “Subject” field, and type your message in the body of the email. You can also add attachments, format the text, and preview the email before sending. Once you are satisfied with the message, click on the “Send” button to send the email.
Email Formats and Attachments
Email formats determine the way the message content is displayed to the recipient. Common email formats include plain text, HTML, and Rich Text Format (RTF). Plain text emails display the message in a simple, unformatted style, while HTML emails allow for formatting and images. RTF emails offer a balance between plain text and HTML, allowing for some formatting while maintaining compatibility with different email clients.
Attachments are files sent along with an email message. They can be various file types, such as documents, images, spreadsheets, or audio files. To attach a file, click on the “Attach” button in the email window and select the file you want to send. The size of the attachment can affect the email’s delivery speed.
Managing Drafts, Folders, and Search
Email applications allow users to save drafts of emails before sending them, organize emails in folders, and search for specific emails. Drafts are saved in a dedicated folder, allowing you to edit or complete the email later. You can create folders to categorize and organize emails, such as “Work,” “Personal,” or “Projects.” The search function enables users to find specific emails by s in the subject line, body, or sender’s name. These features help users manage their emails efficiently and keep track of important messages.
Collaboration and Team Communication
Microsoft Office email is an integral tool for effective team communication and collaboration, enabling seamless information sharing, task delegation, and project management.
Shared Calendars
Shared calendars provide a centralized platform for team members to view and manage appointments, meetings, and deadlines. This visibility ensures everyone is aware of important events and can schedule their activities accordingly.
- Scheduling Meetings: Team members can schedule meetings and invite colleagues, ensuring everyone is on the same page about the time, date, and location.
- Tracking Deadlines: Shared calendars allow for setting reminders and deadlines for tasks, promoting timely completion and project progress.
- Managing Time: By visualizing everyone’s schedules, team members can coordinate their activities and avoid scheduling conflicts, maximizing efficiency.
Shared Mailboxes, Microsoft office email
Shared mailboxes centralize communication for a team, enabling multiple users to access and manage the same inbox. This facilitates streamlined communication and ensures all relevant information is readily available to team members.
- Unified Communication: Team members can easily collaborate on emails, respond to inquiries, and manage correspondence, promoting a cohesive team approach.
- Information Access: Shared mailboxes ensure all team members have access to relevant information, eliminating the need for constant forwarding or duplication of emails.
- Continuity: When a team member is unavailable, others can access the shared mailbox, ensuring uninterrupted communication and responsiveness.
Email Forwarding
Email forwarding enables the automatic redirection of emails from one mailbox to another, facilitating seamless communication and information sharing. This feature allows for efficient delegation and ensures all relevant parties receive critical information.
- Delegation: Email forwarding allows team members to delegate tasks or responsibilities to colleagues, ensuring seamless communication and timely completion.
- Information Sharing: By forwarding emails to relevant team members, individuals can ensure everyone is informed about important updates, project progress, and decisions.
- Streamlined Communication: Email forwarding eliminates the need for manual forwarding or copying, saving time and ensuring efficient communication flow.
Project Management and Task Delegation
Microsoft Office email serves as a valuable tool for managing projects and delegating tasks within teams.
- Task Assignment: Emails can be used to assign specific tasks to team members, outlining expectations, deadlines, and relevant resources.
- Progress Tracking: Emails can be used to request updates on task progress, ensuring project timelines are met and goals are achieved.
- Collaboration and Feedback: Emails facilitate communication and feedback exchange, allowing team members to discuss challenges, provide solutions, and collaborate effectively.
Best Practices for Effective Email Communication
In today’s digital world, email communication is an essential part of our professional and personal lives. It is crucial to understand the best practices for composing professional and effective emails to ensure clear communication, build strong relationships, and maintain a positive image.
Crafting Professional Emails
Crafting professional emails involves more than just typing out a message. It requires careful consideration of your audience, the purpose of your message, and the overall tone and style.
- Use a Professional Subject Line: The subject line is the first impression your email makes. It should be concise, clear, and relevant to the content of your message. For example, instead of “Meeting,” use “Meeting Regarding Project X.”
- Address the Recipient Properly: Always use the recipient’s proper name and title. Avoid using informal greetings like “Hey” or “Yo.”
- Maintain a Professional Tone: While email allows for informal communication, it’s important to maintain a professional tone. Avoid using slang, emojis, or overly casual language.
- Proofread Carefully: Before sending your email, take the time to proofread it carefully for any spelling or grammatical errors. A well-written email reflects professionalism and attention to detail.
Writing Clear and Concise Messages
Clear and concise communication is key to effective email writing. Your message should be easy to understand and get to the point quickly.
- Keep it Short and Sweet: Avoid lengthy paragraphs and unnecessary details. Get to the point of your message quickly and efficiently.
- Use Bullet Points or Numbered Lists: For lengthy messages or information that needs to be easily digestible, use bullet points or numbered lists to break up the text and make it more visually appealing.
- Use Strong Verbs: Use action verbs to make your writing more engaging and impactful. For example, instead of “I will be sending you the report,” use “I am sending you the report.”
- Avoid Jargon: Use language that is understandable to your audience. Avoid using technical jargon or industry-specific terms that they may not be familiar with.
Email Etiquette and Professionalism
Email etiquette is essential for maintaining a positive and professional image.
- Respond Promptly: Respond to emails promptly, especially if they require immediate attention. If you cannot respond immediately, let the sender know when you will be able to.
- Avoid Sending Emails Late at Night or Early in the Morning: It’s generally considered unprofessional to send emails outside of normal business hours.
- Use “Reply All” Judiciously: Only use “Reply All” if all recipients need to see the response.
- Be Mindful of Attachments: Ensure attachments are relevant to the email and are not too large in size.
- Avoid Forwarding Emails Without Permission: Before forwarding an email, ensure you have the sender’s permission to do so.
Closing Summary
From the fundamentals of email composition to the intricacies of advanced features and integrations, this guide provides a holistic understanding of Microsoft Office email. Whether you’re a novice seeking to master the basics or an experienced user looking to enhance your skills, this exploration will empower you to communicate effectively, collaborate seamlessly, and navigate the world of email with confidence.
Microsoft Office email is a powerful tool for communication, but you might need a little extra help with data organization. If you’re looking for a robust spreadsheet program, you can find a free download of MS Excel here.
Once you’ve got Excel, you can easily create charts and tables to analyze your email data, making it even more effective for business and personal use.
