Remote network management platforms have revolutionized the way organizations manage and monitor their networks. These platforms empower IT professionals to oversee and control network devices, applications, and services from any location with an internet connection. By providing a centralized view of the network, remote management platforms streamline operations, enhance security, and optimize performance.
Table of Contents
From simple network monitoring to complex automation tasks, these platforms offer a wide range of features that cater to diverse network environments. This comprehensive guide explores the essential features, types, implementation considerations, and future trends of remote network management platforms, highlighting their significance in the modern digital landscape.
Introduction to Remote Network Management Platforms
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, managing vast and complex networks has become increasingly challenging. Remote network management platforms have emerged as essential tools for organizations of all sizes, offering efficient and centralized control over their network infrastructure.
Remote network management platforms are software applications that enable administrators to monitor, configure, and troubleshoot network devices remotely. They provide a single point of access for managing various network components, including routers, switches, firewalls, and servers.
Evolution of Remote Network Management
Remote network management has undergone a significant evolution over the years, driven by technological advancements and changing network demands.
Initially, network management was primarily performed on-site, requiring physical access to devices. This approach was time-consuming, inefficient, and often disruptive to network operations.
With the advent of the internet and the development of remote access protocols, remote network management became a reality. Early remote management tools were limited in functionality and often required specialized hardware and software.
Today, cloud-based remote network management platforms offer a comprehensive suite of features, including:
- Real-time network monitoring
- Device configuration and management
- Performance analysis and reporting
- Security event logging and alerting
- Automated network troubleshooting
These platforms are highly scalable and can be customized to meet the specific needs of different organizations.
Benefits of Utilizing Remote Network Management Platforms
Remote network management platforms offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Efficiency: Remote management eliminates the need for on-site visits, reducing downtime and allowing administrators to manage network devices from anywhere with an internet connection. This streamlined approach saves time and resources.
- Enhanced Security: Remote network management platforms can help organizations improve their security posture by providing centralized control over network devices and access points. These platforms can also be used to enforce security policies and monitor for suspicious activity.
- Reduced Costs: By automating tasks and reducing the need for on-site personnel, remote network management platforms can help organizations significantly reduce their operating costs.
- Increased Network Availability: Remote network management platforms allow administrators to proactively monitor network performance and identify potential issues before they cause disruptions. This proactive approach helps ensure network uptime and availability.
- Simplified Management: Remote network management platforms consolidate network management tasks into a single, user-friendly interface, simplifying complex operations and reducing the workload for network administrators.
Key Considerations for Selecting a Remote Network Management Platform
Choosing the right remote network management platform is crucial for ensuring efficient and secure network operations. It’s a decision that should not be taken lightly, as the platform will play a significant role in your network’s performance, security, and overall manageability.
Factors Influencing Platform Selection
Several key factors should be considered when selecting a remote network management platform. These factors can help narrow down your choices and ultimately lead you to a platform that best meets your specific needs.
- Network Size and Complexity: The size and complexity of your network are crucial considerations. A small network with simple infrastructure may require a less feature-rich platform compared to a large, complex network with multiple locations and diverse devices.
- Budget: Your budget constraints will influence the type of platform you can afford. Some platforms offer free or freemium versions, while others come with a subscription fee based on the number of devices or features you require.
- Security Requirements: Network security is paramount, and your platform should offer robust security features, such as authentication, encryption, and access control. The platform should comply with industry security standards and regulations, such as HIPAA or PCI DSS, depending on your specific needs.
Platform Features and Capabilities
Once you have a clear understanding of your network requirements, you can start evaluating platforms based on their features and capabilities. Some key aspects to consider include:
- Scalability: The platform should be able to scale with your growing network needs. It should be able to handle an increasing number of devices, users, and network traffic without impacting performance.
- Integration Capabilities: The platform should seamlessly integrate with your existing network infrastructure and other IT systems. This ensures smooth data flow and eliminates the need for manual data entry or reconciliation.
- Vendor Support: Reliable vendor support is essential for resolving issues and maximizing platform usage. Consider the vendor’s reputation, response times, and availability of documentation and training materials.
Popular Remote Network Management Platforms
The following table provides an overview of popular remote network management platforms, highlighting their key features, pros, cons, and target audience:
| Platform | Key Features | Pros | Cons | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM) | Network performance monitoring, traffic analysis, capacity planning, and troubleshooting | Comprehensive feature set, user-friendly interface, affordable pricing | Can be complex for beginners, limited automation capabilities | Small to medium-sized businesses, IT professionals |
| Datadog | Network performance monitoring, infrastructure monitoring, log management, and security monitoring | Cloud-based platform, extensive integrations, real-time monitoring | Higher pricing than some alternatives, can be complex to configure | Large enterprises, DevOps teams, cloud-native environments |
| ManageEngine OpManager | Network performance monitoring, device management, and fault management | Affordable pricing, comprehensive device support, user-friendly interface | Limited automation capabilities, less advanced features compared to some competitors | Small to medium-sized businesses, IT professionals |
| Auvik | Network mapping, device discovery, performance monitoring, and configuration management | Easy-to-use interface, automated network discovery, affordable pricing | Limited advanced features, fewer integrations compared to some competitors | Small to medium-sized businesses, MSPs |
| PRTG Network Monitor | Network performance monitoring, device monitoring, and reporting | Affordable pricing, user-friendly interface, extensive sensor library | Limited automation capabilities, less advanced features compared to some competitors | Small to medium-sized businesses, IT professionals |
Implementation and Deployment of Remote Network Management Platforms
Deploying a remote network management platform requires a systematic approach to ensure smooth integration and optimal performance. This involves careful planning, configuration, and integration with existing network infrastructure.
Steps Involved in Deploying a Remote Network Management Platform
The deployment process typically involves several key steps:
- Planning and Design: This phase involves defining the scope of the deployment, identifying the target network devices, and selecting the appropriate remote network management platform. It’s essential to consider factors such as network size, complexity, and specific management requirements.
- Installation and Configuration: Once the platform is selected, it needs to be installed on a suitable server or virtual machine. This involves configuring the platform’s settings, such as network credentials, user accounts, and access control policies.
- Device Discovery and Integration: The platform needs to discover and integrate with the target network devices. This may involve configuring device-specific settings, such as SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) or SSH (Secure Shell) access, to enable communication and data collection.
- Policy and Alert Configuration: Defining monitoring policies and setting up alert thresholds are crucial for proactive network management. This involves configuring the platform to monitor specific network parameters, such as bandwidth utilization, device availability, and security events, and trigger alerts when predefined thresholds are exceeded.
- Testing and Validation: Before deploying the platform in production, it’s essential to test and validate its functionality. This involves simulating real-world scenarios and verifying that the platform can effectively monitor and manage the network.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Once testing is complete, the platform can be deployed in production. Ongoing monitoring is essential to ensure the platform’s stability, performance, and effectiveness in managing the network.
Best Practices for Configuring and Integrating the Platform
Optimizing the platform’s configuration and integration with existing network infrastructure is essential for seamless operation and efficient management:
- Use standardized protocols: Employing standard protocols such as SNMP, SSH, and Telnet simplifies device integration and reduces configuration complexity.
- Implement strong security measures: Secure access to the platform and network devices using robust authentication mechanisms, encryption, and access control policies.
- Optimize performance: Consider factors such as network bandwidth, server resources, and device polling intervals to minimize performance impact on the network.
- Ensure proper documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of the platform’s configuration, network devices, and management policies to facilitate troubleshooting and future maintenance.
- Provide user training: Train network administrators on using the platform’s features and functionalities to maximize its benefits and ensure effective network management.
Tips for Optimizing Performance and Ensuring Seamless Operation
To ensure optimal performance and seamless operation, consider the following tips:
- Regularly update the platform: Keep the platform software and firmware up-to-date to benefit from security patches, performance enhancements, and new features.
- Monitor resource utilization: Regularly monitor server resources, such as CPU, memory, and disk space, to identify potential bottlenecks and proactively address them.
- Optimize polling intervals: Adjust device polling intervals based on the criticality of the monitored parameters. Frequent polling for critical devices and less frequent polling for less critical devices can optimize performance.
- Implement redundancy and failover mechanisms: Ensure high availability by configuring redundant servers and failover mechanisms to minimize downtime in case of server failures.
- Utilize automated tasks: Automate repetitive tasks, such as device configuration updates or report generation, to reduce manual effort and improve efficiency.
Use Cases for Remote Network Management Platforms
Remote network management platforms are versatile tools that can be used to manage and monitor networks remotely, offering significant benefits in terms of efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Their applications extend across various industries and business functions, enabling organizations to optimize their network performance, troubleshoot issues, and ensure security.
Network Troubleshooting
Remote network management platforms are essential for network troubleshooting, enabling IT professionals to identify and resolve network issues quickly and efficiently. By providing real-time network performance data, these platforms allow IT teams to pinpoint the root cause of network problems, such as slow connections, network outages, or security breaches.
- Real-time monitoring and alerting: Platforms provide real-time monitoring of network devices and traffic, generating alerts when anomalies or performance issues are detected. This allows for proactive troubleshooting and minimizes downtime.
- Log analysis and correlation: These platforms can collect and analyze network logs from various devices, correlating events to identify the root cause of problems. This helps in pinpointing the source of issues, such as faulty hardware, software bugs, or configuration errors.
- Remote access and configuration: Platforms allow IT professionals to remotely access and configure network devices, enabling them to troubleshoot issues and implement solutions without physically being on-site.
Performance Optimization
Remote network management platforms play a crucial role in optimizing network performance, ensuring smooth operations and maximizing network utilization. By providing comprehensive network performance data and insights, these platforms empower IT teams to identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall network efficiency.
- Network traffic analysis: Platforms provide detailed insights into network traffic patterns, allowing IT teams to identify bandwidth-intensive applications or devices and optimize resource allocation. This helps ensure smooth network performance, even during peak traffic periods.
- Performance monitoring and reporting: These platforms monitor key network performance metrics, such as latency, throughput, and packet loss, generating reports that highlight potential areas for improvement. This data helps IT teams to identify bottlenecks and optimize network configuration for optimal performance.
- Capacity planning: Platforms assist in capacity planning by providing insights into current network utilization and future growth trends. This allows organizations to proactively scale their network infrastructure to meet evolving business demands and prevent performance degradation.
Security Incident Response
Remote network management platforms are vital for security incident response, enabling organizations to detect, analyze, and respond to security threats quickly and effectively. By providing real-time security monitoring, threat intelligence, and automated response capabilities, these platforms enhance security posture and minimize the impact of security incidents.
- Security event monitoring and alerting: Platforms monitor network activity for suspicious patterns and security threats, generating alerts when potential security incidents are detected. This enables organizations to respond promptly to threats, minimizing their impact on business operations.
- Threat intelligence and analysis: These platforms provide access to threat intelligence feeds and analysis tools, allowing IT teams to stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities. This helps organizations to proactively mitigate risks and enhance their security posture.
- Automated security response: Platforms can automate security response actions, such as blocking malicious traffic, isolating infected devices, or initiating incident response procedures. This reduces the time required to respond to security threats, minimizing their impact on business operations.
Network Automation and Self-Healing, Remote network management platform
Remote network management platforms are instrumental in enabling network automation and self-healing capabilities, simplifying network management and reducing human error. By automating routine tasks and implementing self-healing mechanisms, these platforms improve network efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance operational agility.
- Automated configuration management: Platforms automate configuration tasks, such as device provisioning, software updates, and security policy enforcement. This reduces human error and ensures consistent network configuration across devices.
- Self-healing capabilities: Platforms can implement self-healing mechanisms that automatically detect and resolve network issues, such as restarting faulty devices, rerouting traffic, or applying corrective actions. This minimizes downtime and improves network resilience.
- Workflow automation: Platforms can automate complex network management workflows, such as incident response procedures, change management processes, and capacity planning tasks. This improves operational efficiency and reduces manual effort.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples: Remote Network Management Platform
Remote network management platforms have revolutionized how organizations manage their networks, offering a range of benefits from improved efficiency and security to enhanced scalability and reduced costs. Examining real-world implementations provides a deeper understanding of the practical applications and impact of these platforms.
Case Studies Illustrating Successful Implementations
Several companies across different industries have successfully deployed remote network management platforms, achieving significant improvements in their network operations. The following case studies showcase the diverse applications and benefits of these platforms.
| Company | Industry | Platform Used | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acme Corporation | Manufacturing | SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor | Reduced network downtime by 50%, improved network visibility, and streamlined troubleshooting processes. |
| Global Retail Inc. | Retail | Cisco Meraki SD-WAN | Enhanced network security, optimized application performance, and simplified branch office management. |
| Zenith Healthcare | Healthcare | Datadog Network Performance Monitoring | Improved network reliability, reduced latency for critical medical applications, and facilitated compliance with HIPAA regulations. |
Real-World Examples Demonstrating the Benefits of Remote Network Management Platforms
Beyond the case studies, numerous examples illustrate the tangible benefits of using remote network management platforms.
“Our remote network management platform has allowed us to proactively identify and address network issues before they impact our operations. We have significantly reduced downtime and improved overall network performance.” – Network Manager, XYZ Company
Another example is a large financial institution that deployed a remote network management platform to secure its distributed network infrastructure. The platform provided real-time visibility into network traffic, enabled automated threat detection and response, and helped the organization comply with regulatory requirements.
“Our remote network management platform has been instrumental in enhancing our network security posture. We can now detect and respond to threats in real-time, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of our sensitive data.” – Chief Information Security Officer, ABC Bank
Best Practices for Effective Remote Network Management
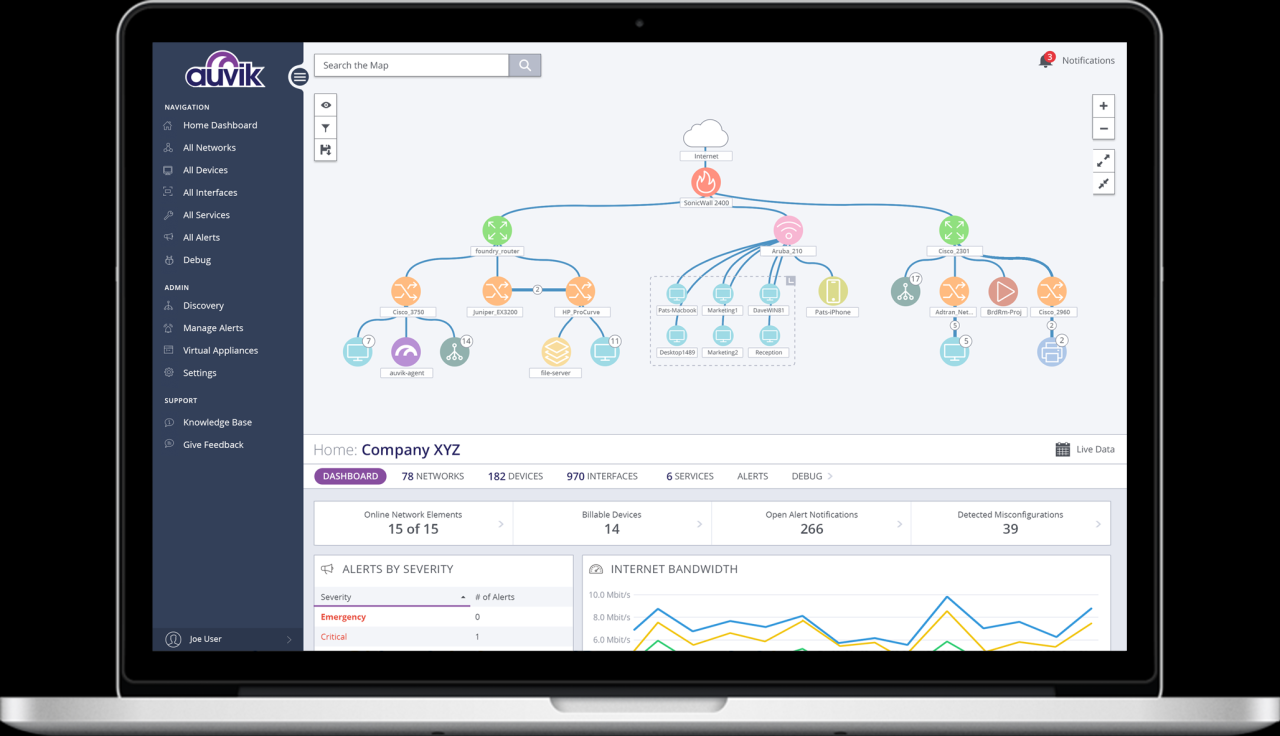
Remote network management platforms offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency, scalability, and accessibility. However, to maximize their benefits, adopting best practices is crucial. These practices encompass a holistic approach to managing and monitoring networks remotely, ensuring network security, availability, and performance while facilitating effective troubleshooting and preventative measures.
Network Security
Implementing robust security measures is paramount when managing networks remotely. Remote access exposes networks to potential vulnerabilities, making it essential to establish a layered security approach.
- Strong Authentication and Authorization: Employ multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all remote access, requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as passwords, tokens, or biometrics. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict user privileges based on their roles and responsibilities, limiting access to only necessary resources.
- Secure Network Connectivity: Utilize secure protocols like SSH and HTTPS for remote connections, encrypting data transmission and protecting against eavesdropping. Implement virtual private networks (VPNs) to create secure tunnels between remote users and the network, further enhancing data confidentiality.
- Regular Security Audits and Patching: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats. Implement a comprehensive patch management strategy to ensure all devices and software are updated with the latest security patches, mitigating known vulnerabilities and reducing the risk of exploits.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Deploy intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and block potential attacks. Configure these systems to analyze network traffic patterns, identify anomalies, and trigger alerts or block malicious connections.
Network Availability
Ensuring continuous network availability is critical for smooth operations. Remote management platforms offer tools to monitor network performance and proactively address potential issues.
- Real-time Monitoring and Alerting: Implement real-time network monitoring tools that provide comprehensive visibility into network performance, including bandwidth usage, latency, and device status. Configure alerts to notify administrators of critical events, such as device failures, network outages, or performance degradations, enabling prompt intervention and minimizing downtime.
- Redundancy and Failover Mechanisms: Implement redundant network components, such as dual internet connections, redundant routers, and failover servers, to ensure continued network operation even if one component fails. Configure failover mechanisms to automatically switch to backup components, minimizing disruption to network services.
- Network Capacity Planning and Optimization: Proactively assess network capacity and plan for future growth. Monitor network utilization and identify potential bottlenecks. Optimize network configurations, such as adjusting bandwidth allocation, prioritizing traffic, and implementing load balancing, to improve performance and ensure sufficient capacity for current and future demands.
Network Performance
Optimizing network performance is essential for delivering a seamless user experience and maximizing network efficiency. Remote management platforms provide tools to analyze network traffic, identify performance bottlenecks, and optimize network configurations.
- Performance Monitoring and Analysis: Utilize network performance monitoring tools to gather real-time data on network traffic patterns, latency, packet loss, and other performance metrics. Analyze this data to identify potential bottlenecks, such as congested network segments, slow devices, or inefficient routing paths.
- Traffic Shaping and Prioritization: Implement traffic shaping and prioritization mechanisms to manage network traffic effectively. Allocate bandwidth based on application requirements, prioritize critical traffic, and limit bandwidth-intensive applications during peak hours to ensure smooth operation for essential services.
- Network Optimization Tools: Leverage network optimization tools, such as path optimization algorithms, to identify and resolve routing inefficiencies. Implement network optimization techniques, such as TCP optimization and congestion control mechanisms, to improve data transmission efficiency and minimize network latency.
Troubleshooting and Preventative Measures
Effective troubleshooting is crucial for addressing network issues promptly and minimizing downtime. Remote management platforms provide tools to diagnose network problems, identify root causes, and implement corrective actions.
- Centralized Logging and Reporting: Implement centralized logging and reporting systems to capture network events, error messages, and performance metrics. This provides a comprehensive view of network activity, enabling administrators to quickly identify and analyze potential issues.
- Remote Access and Control: Utilize remote access and control tools to remotely manage and troubleshoot network devices. This allows administrators to diagnose problems, configure devices, and apply fixes without physically accessing the equipment.
- Automated Scripting and Task Automation: Implement automated scripting and task automation to streamline repetitive tasks, such as device configuration, software updates, and security checks. This reduces the risk of human error and improves efficiency.
Network Documentation and Knowledge Base
Maintaining comprehensive network documentation is essential for effective remote management.
- Network Topology Diagrams: Create detailed network topology diagrams that depict the physical and logical connections between network devices, including routers, switches, servers, and other components. This documentation provides a clear understanding of the network infrastructure and facilitates troubleshooting.
- Device Configuration Files: Store and manage device configuration files, including router configurations, switch configurations, and firewall rules. This documentation ensures consistency across network devices and allows for easy replication or rollback of configurations.
- Network Policies and Procedures: Document network policies, security procedures, and operational guidelines. This ensures consistency in network management practices and provides a reference point for troubleshooting and incident response.
Resources and Tools for Remote Network Management
Successfully managing a network remotely requires access to a variety of resources and tools. These resources can help you stay updated on industry best practices, troubleshoot issues, and implement new technologies.
Industry Publications and Online Forums
Industry publications and online forums offer valuable insights and knowledge sharing opportunities for network professionals. These resources provide access to expert opinions, case studies, and discussions on emerging trends in remote network management.
- Network World: A leading publication covering network technology, providing news, analysis, and insights on remote network management practices.
- Cisco Networking Academy: Offers comprehensive training programs and resources on network management, including remote network management concepts and technologies.
- Network Management Forum (NMF): A non-profit organization focused on promoting standards and best practices for network management, including remote management.
- Network Engineering Stack Exchange: An online forum where network engineers can ask questions, share knowledge, and discuss remote network management challenges.
- Reddit’s r/networking: A subreddit dedicated to networking professionals, offering discussions and insights on remote network management.
Remote Network Management Tools and Software
Remote network management tools and software streamline network monitoring, configuration, and troubleshooting tasks. These tools provide centralized dashboards, automated tasks, and real-time insights into network performance.
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor: Offers comprehensive network monitoring and performance analysis capabilities, including remote management features.
- Datadog: Provides cloud-based monitoring and management solutions, including remote network management capabilities for hybrid and cloud environments.
- ManageEngine OpManager: Offers network monitoring, performance analysis, and remote management capabilities, with support for various network devices.
- Auvik: Provides a cloud-based network management platform with automated network discovery, mapping, and remote configuration capabilities.
- PRTG Network Monitor: Offers comprehensive network monitoring and management features, including remote access and control of network devices.
Final Review
Remote network management platforms are a critical component of modern network infrastructure, offering organizations the ability to manage and optimize their networks effectively and efficiently. As technology continues to evolve, these platforms will play an increasingly vital role in enabling secure, reliable, and scalable network operations. By leveraging the power of remote network management, organizations can enhance their network performance, strengthen security posture, and drive business growth.
A remote network management platform provides centralized control over your IT infrastructure, allowing you to manage devices, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues from anywhere. MSPs often rely on powerful solutions like msp rmm to streamline their operations and provide exceptional service to their clients.
These platforms empower MSPs to manage multiple client networks efficiently, enhancing security and ensuring optimal performance.
